The Battle of the Little Bighorn is one of the highest-profile events still shaping North American history. It’s an intensely studied military and social conflict. Yet, the main mystery of what occurred in June of 1876 on the Montana plains seems unsolved. That’s why—not how—the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne warriors were able to strategically and tactically annihilate five United States Army 7th Cavalry companies under Lieutenant Colonel George Armstrong Custer’s command and severely maul other soldiers in his regiment.
The Battle of the Little Bighorn is one of the highest-profile events still shaping North American history. It’s an intensely studied military and social conflict. Yet, the main mystery of what occurred in June of 1876 on the Montana plains seems unsolved. That’s why—not how—the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne warriors were able to strategically and tactically annihilate five United States Army 7th Cavalry companies under Lieutenant Colonel George Armstrong Custer’s command and severely maul other soldiers in his regiment.
The core reason—the root cause—of why Custer really lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn hasn’t been identified by historians. They’ve overlooked the Sun Dance effect—the psychological and spiritual impact of the warriors’ cultural unity led by Lakota Chief Sitting Bull. This book outlines why the Lakota Sioux Sun Dance had such a powerful effect on the warriors’ will to win and why this sacred ceremony was the root cause of Custer’s demise.
That about 268 United States Army soldiers and approximately 40-50—maybe as many as 100—Native American civilians died in a brutally violent battle at a valley along the Little Bighorn River is a well-documented historical fact. Over the years, Custermania books saturated the non-fiction historical market. They’ve dissected practically every explainable part of the action.
 Except for one. That’s where this book is different. It says Custer lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn because of the immense psychological effect the Native Americans’ ceremonial Sun Dance had on willing their people to win. Mentally, the Sun Dance made the warriors far better prepared to fight than the soldiers. In their minds, the warriors knew they would win. They were convinced that all they had to do was get the job done.
Except for one. That’s where this book is different. It says Custer lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn because of the immense psychological effect the Native Americans’ ceremonial Sun Dance had on willing their people to win. Mentally, the Sun Dance made the warriors far better prepared to fight than the soldiers. In their minds, the warriors knew they would win. They were convinced that all they had to do was get the job done.
It was an amazing cohesiveness of combined will and unwavering belief that mobilized the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne people to attack the United States Army. They defended themselves, and their very existence, through forced aggression. Nowhere—at any time—did Euro-American authorities expect “savages and inferiors” would be superior in spiritual, strategic and tactical warfighting. At the Battle of the Little Bighorn, Lt. Col. George Custer, and the 7th Cavalry he controlled, was mentally outclassed and defeated. It was because of the Sun Dance.
The Sioux and the 7th Engage
What happened at the Battle of the Little Bighorn is George Custer headed the U.S. Army 7th Cavalry regiment to find and engage a nomadic camp of Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne Native Americans spiritually invigorated by Hunkpapa Lakota Chief Sitting Bull. The military mission’s objective was to force free-roaming native people onto reservations so European-Americans could steal their remaining land. For the indigenous people, their objective was self-defense and preserving a traditional way of life.
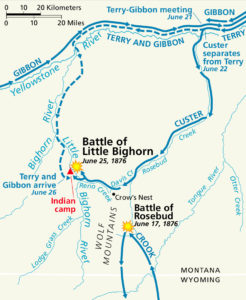 Custer’s cavalry found Sitting Bull’s camp in a valley along the Little Bighorn River. The village was far larger than Custer anticipated—possibly up to 10,000 people. Custer chose to attack immediately—despite the massive population and having no idea of the resolve warriors had to fight—rather than conduct reconnaissance and prepare a proper battle plan or attempt negotiations. Historically, the disastrous results for the soldiers are well-documented. The Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne alliance overwhelmed and soundly defeated the U.S. Army.
Custer’s cavalry found Sitting Bull’s camp in a valley along the Little Bighorn River. The village was far larger than Custer anticipated—possibly up to 10,000 people. Custer chose to attack immediately—despite the massive population and having no idea of the resolve warriors had to fight—rather than conduct reconnaissance and prepare a proper battle plan or attempt negotiations. Historically, the disastrous results for the soldiers are well-documented. The Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne alliance overwhelmed and soundly defeated the U.S. Army.
The battle circumstances are well recorded, but the real reason—the root cause—why the warriors cohesively gelled and so effectively destroyed Custer’s troops was never distinctly identified. It was ignored. Research through carefully-applied root cause analysis techniques show the enormous positive effect Sitting Bull’s ceremonial Sun Dance—performed shortly before the battle—had on his people. Sitting Bull experienced a victory vision during the Sun Dance that mentally and spiritually prepared his warriors for combat.
Psychologically, the warriors knew there was a fight coming. They were convinced they’d be victorious. It wasn’t only their superior numbers. It wasn’t just the terrain and their home-turf advantage. And, it wasn’t simply their weapons and skillful tactics.
Those were factors, for sure. However, it was their collective mindset—their commitment to engage the soldiers—that gave them overwhelming and superior psychological power. Combined with physical cohesiveness, this allowed the warriors to stunningly defeat the United States Army. The 7th Cavalry soldiers never had a fighting chance.
Two Reasons for this Book
There’s been more written about the Little Bighorn confrontation than any other single American conflict, except possibly the Battle of Gettysburg—certainly more than Pearl Harbor and D-Day. Fascination about the Greasy Grass fight, as Native Americans call it, or Custer’s Last Stand as it’s also known, has never waned. There are plenty of factors for continual interest. Perhaps as many factors as there are books.
So, why this book when so many others exist? Why enter a saturated Custermania market of Little Bighorn writing when so many speculative theories and analytical examinations already exist? There are two reasons.
 First, the current plight of the plains indigenous people and other Native Americans is directly attributed to white society actions that caused events like the Battle of the Little Bighorn. As military battles go, the Little Bighorn was a small skirmish though it had crushing ramifications. The battle’s aftermath set the stage for European-American and Native-American relations spanning more than a century.
First, the current plight of the plains indigenous people and other Native Americans is directly attributed to white society actions that caused events like the Battle of the Little Bighorn. As military battles go, the Little Bighorn was a small skirmish though it had crushing ramifications. The battle’s aftermath set the stage for European-American and Native-American relations spanning more than a century.
The Battle of the Little Bighorn still has an impact on today’s Native-Euro American relationships. It’s exceptionally important for people to understand the wrongs inflicted on Native Americans by European-based society. Everyone can benefit from a deeper understanding of other cultures, especially a culture as spiritually advanced as the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne were in the nineteenth century. That’s this book’s primary purpose.
Secondly, the core reason—the root cause—of why Lieutenant Colonel George Armstrong Custer and his 7th Cavalry lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn has never been precisely identified and articulated. Finding the root cause is vital as it solves a long-standing historical mystery and resolves many misconceptions. It produces a better understanding of this high-profile event and a greater appreciation for Native American culture.
 Historians focus on issues like how drastically outnumbered Custer was and how he charged an attack without sufficient intelligence to know the terrain and his odds. Often, the main reason cited for Custer’s defeat is because he divided his command into smaller units unable to support one another. Poor communication between soldier groups under Custer’s command is another identified downfall.
Historians focus on issues like how drastically outnumbered Custer was and how he charged an attack without sufficient intelligence to know the terrain and his odds. Often, the main reason cited for Custer’s defeat is because he divided his command into smaller units unable to support one another. Poor communication between soldier groups under Custer’s command is another identified downfall.
Many suggest Custer’s ego played a big role in this recklessness—how his lust for glory overshadowed his caution and leadership responsibility to protect his command. Historians and Custer buffs also identify how regiment infighting, hunger and malnutrition, fatigue, fear, confusion and chaos, drunkenness, lack of discipline, low morale, poor training and weapons malfunction contributed to Custer’s defeat. Some even suggest Custer disobeyed orders.
All these factors were likely influences on the battle’s outcome. Probably most, combined, contributed to the 7th’s defeat. But, what really caused the warriors to win—the underlying root cause—was their mental state.
Sitting Bull’s Sun Dance Vision
It started with Sitting Bull’s vision at the Sun Dance. Sitting Bull held a multi-day cultural ceremony at Deer Medicine Rocks along the Rosebud River which is one watershed east of the Little Bighorn. This was in mid-June, 1876, about 10 days before the Little Bighorn battle. After enduring enormous pain through self-mutilation and sensory deprivation, Sitting Bull publicly danced in the blazing sun until he dropped from exhaustion.
 Sitting Bull had a vision where mounted U.S. soldiers fell upside down from the sky into their camp. He interpreted this as a message from Wakan Tanka, or the Great Spirit Creator, that American soldiers would attack them but be annihilated by the warriors in a victorious battle.
Sitting Bull had a vision where mounted U.S. soldiers fell upside down from the sky into their camp. He interpreted this as a message from Wakan Tanka, or the Great Spirit Creator, that American soldiers would attack them but be annihilated by the warriors in a victorious battle.
Sitting Bull correctly predicted the army’s loss and the warriors’ win. To the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne people, this was a divine message and a guarantee for victory. It psyched the warriors into a supercharged and unbeatable mental state.
The key to understanding this root cause is to appreciate the effect of Sitting Bull’s leadership and how Sitting Bull conducted himself in the Sun Dance held just days before the battle. It psychically and spiritually equipped the warriors to win. Sitting Bull’s credibility and integrity caused unity—cohesion with all native tribe occupants of the massive village including women, elders and other non-combatants.
Because their belief in winning was so strong—so overwhelmingly powerful—warriors went into battle with an unbreakable mental conviction. They knew they couldn’t lose. It was just a matter of exercising the process. That wasn’t the case with United States Army’s 7th Cavalry soldiers, and that’s why Custer really lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn.
Authority to Write This Book
Why am I an authority to write this book? First, I’m not a historian. I’m a retired investigator with experience as a homicide cop, then as a forensic coroner, now as a crime writer and researcher. I’m also formally trained in conducting a Root Cause Analysis of crime and accident events by the industry’s authority, Think Reliability.
I’ve always had an interest in the Battle of the Little Bighorn. I also have an intense interest and some experience in Native American spirituality after being exposed to the sweat lodge culture. It’s part of my curiosity to try and make some sense out of interconnected consciousness… but that’s for another book.
I decided to write a post on my blog site www.DyingWords.net about applying a root cause analysis to the Little Bighorn battle. To my surprise—my astonishment, you could say—I found the root cause of why Custer lost wasn’t the numbers, the tactics, the terrain, the weapons or even George Custer’s inflated ego and erroneous decision about ignoring reconnaissance and splitting his forces. These were factors, for sure. But no matter how I analyzed it, the arrows kept pointing at the Sun Dance.
What started as a blog post turned into this book. It began with fact research that took me down a historical rabbit hole, through tightly-connected strategical and tactical tunnels, then into a labyrinth of fascinating insights about military procedure, native culture and overall human conditions. Most blog posts take a few hours to research and write. This book took two years and I want to share it with you.
 While the root cause of why Custer really lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn appears obvious, it seems this simple explanation escaped most historians. They paid little attention to the Sun Dance’s important influence in every publication and film I’ve seen. It’s fair to say that no other work details the Sun Dance connection to the Battle of the Little Bighorn. If it exists, I haven’t found it. If it does, I hope you can share.
While the root cause of why Custer really lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn appears obvious, it seems this simple explanation escaped most historians. They paid little attention to the Sun Dance’s important influence in every publication and film I’ve seen. It’s fair to say that no other work details the Sun Dance connection to the Battle of the Little Bighorn. If it exists, I haven’t found it. If it does, I hope you can share.
Doing a Root Cause Analysis
Conducting a root cause analysis isn’t difficult. It’s actually a common sense approach to looking at an outcome, or a negative-impact loss situation, and getting to the root reason for what caused it. In the crime business, it helps identify the motive and points out the suspect. In the accident business, it identifies a danger and seeks to prevent another mishap by eliminating the cause. Determining a root cause also identifies responsibility and accountability for negligent actions.
The same principles apply whether you’re cause mapping something as simple as a fall down the stairs, something fairly routine like a vehicle accident, something serious like a homicide, or something as highly-complex as the Battle of the Little Bighorn. You keep asking, “Why?” till you run out of answers. That’ll give you the root cause.
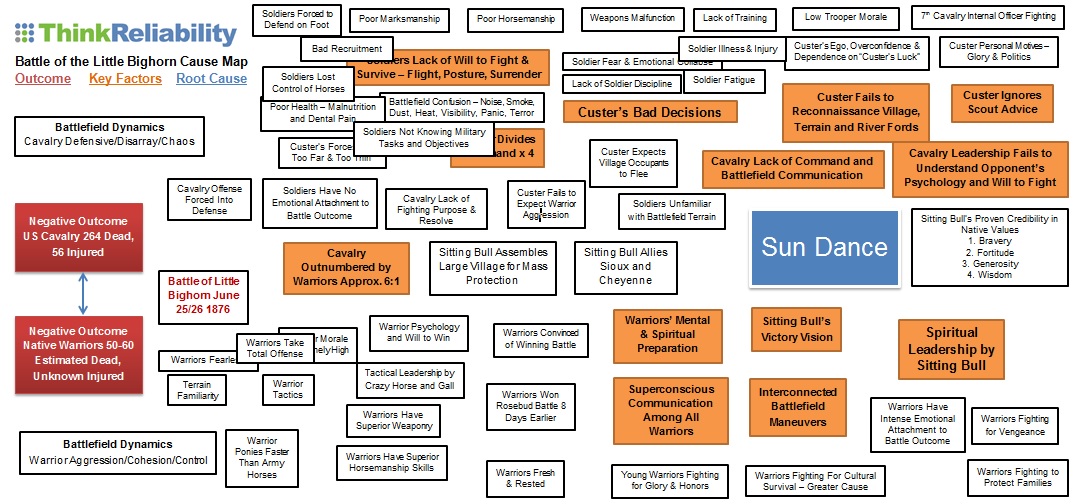
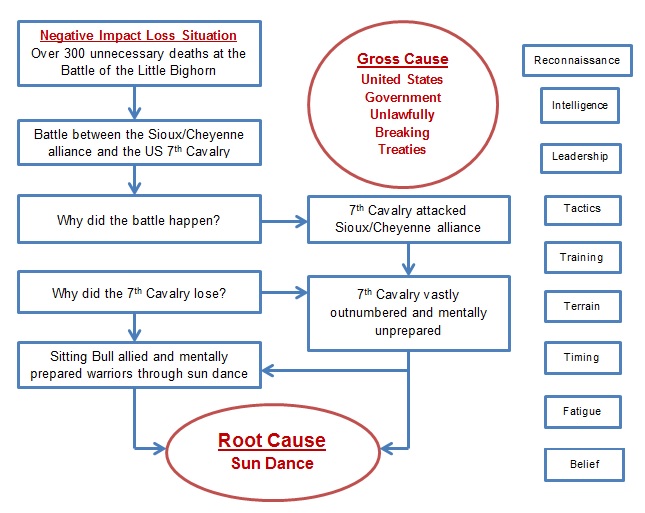
Root cause analysis is also called cause and effect analysis or fish-boning. You state your effect like “over 300 unnecessary deaths at the Little Bighorn” and ask why that happened. Your first cause answer will be “a battle between the Lakota Sioux/Northern Cheyenne alliance and the U.S. Cavalry”. Your next question might be “why did the Sioux and Cheyenne ally?” The answer is because “Sitting Bull pulled them together for mutual protection through the Sun Dance ritual”. Another question is “Why were the soldiers so outnumbered?” The obvious answer is because “the Sioux and Cheyenne made a pact sealed by the Sun Dance to ally for safety in numbers to prevent being attacked by soldiers”.
This alliance and the huge number of warriors coming together happened because Sitting Bull realized the dangers from a direct attack on his camp by U.S. soldiers. His spiritual leadership allied all available native people into one huge village. The alliance mechanism mentally bonded them.
Sitting Bull galvanized this through the traditional Sun Dance ceremony and demonstrating the four sacred Lakota principles of bravery, fortitude, generosity and wisdom. At the Sun Dance, Sitting Bull reaffirmed his mental strength, physical endurance and unwavering personal commitment to his peoples’ welfare. Again, this points to the Sun Dance ritual as the common denominator for bonding the people.
You need to take every pertinent and contributing factor you can find into account when doing a root cause analysis. In the case of the Little Bighorn, that includes every relevant contributor or detractor on both sides of the battlefield. For the soldiers, there were leadership problems, a lack of training and proficiency in horsemanship, poor shooting ability, fatigue, pain, hunger, thirst, bad morale and regiment infighting, poor or non-existent reconnaissance and intelligence as well as severe tactical mistakes, fear, terror, emotional collapse and disorder leading to chaos and a complete command breakdown. Additionally, the soldiers didn’t have personal skin in the game until it came to the end. Then, it was too late to escape.
Native American Warrior Superiority
The list of contributing factors is also extensive, but it comes around to Native American warrior superiority in almost every way. They had the terrain on their side or home field advantage. The warriors had extensive weaponry and the skills to use it. And they also had total skin in the game from the start. Their cultural and personal survival depended on winning. But, most of all, the warriors had the unswayable will to win and the incredible ability to communicate through some form of consciousness-based interconnection across five miles of rugged battlefield.
 Conventional western science doesn’t begin to address or understand this phenomenon. Somehow, it’s part of the Lakota and Cheyenne cultural complexity. That’s firmly formed, anchored and nurtured in the Sun Dance ritual. This reality is foreign to most Euro-Americans, but many people in today’s Native American societies understand this power and still practice the principles.
Conventional western science doesn’t begin to address or understand this phenomenon. Somehow, it’s part of the Lakota and Cheyenne cultural complexity. That’s firmly formed, anchored and nurtured in the Sun Dance ritual. This reality is foreign to most Euro-Americans, but many people in today’s Native American societies understand this power and still practice the principles.
Finally, you’ll get to the question about mental preparedness. There’s no other answer than the Sun Dance. Clearly, the root cause of why Custer really lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn is due to Sitting Bull’s leadership in mentally preparing his warriors to fight. Not only were they incredibly psyched-up, but these fighting men were desperately protecting their families and their way of life. Their willpower and their ability to cooperate on the battlefield completely overpowered the 7th Cavalry. The Native Americans turned the table on the army, immediately and completely throwing the cavalry’s offensive charge into a defensive rout.
Building a Cause Map
On a cause map produced in a spreadsheet, the effect and cause boxes connect with arrows. My actual cause map for the Battle of the Little Bighorn on the Think Reliability Excel sheet is far more detailed. It’s available at a link on my website where you can print it out, but it looks something like this concept.
Root cause analysis theory is straightforward. You keep drilling down till you run out of questions. In some cases, there can be multiple root causes. With the Little Bighorn battle, you can make the argument that Custer made a gross tactical error by dividing his command against a vastly superior force. He failed to anticipate the warrior numbers and resolve to fight. History proves that quite right. Ultimately, Custer failed to properly assess his battle challenges and options.
In fact, the mentality of the entire United States Army hierarchy for capturing “hostile” natives was to prevent the villages from breaking up and fleeing. That’s what they assumed would happen. It wasn’t just Custer who got the native people wrong.
 Not one of them—from President Ulysses S. Grant to William Sherman, General of the Army, to General Philip Sheridan, Commander of the Missouri Department, to General Alfred Terry, leader of the fateful 1876 Dakota-Montana-Wyoming summer campaign—gave any thought that the native people would do anything but flee or cut & run. Custer, like all his superiors, went into the campaign with the entire concern that his challenge would be locating and containing the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne to prevent them from running.
Not one of them—from President Ulysses S. Grant to William Sherman, General of the Army, to General Philip Sheridan, Commander of the Missouri Department, to General Alfred Terry, leader of the fateful 1876 Dakota-Montana-Wyoming summer campaign—gave any thought that the native people would do anything but flee or cut & run. Custer, like all his superiors, went into the campaign with the entire concern that his challenge would be locating and containing the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne to prevent them from running.
The challenge with doing a proper and thorough root cause analysis with something as intertwined as the Battle of the Little Bighorn is getting reliable information. Determining the facts is crucial before putting them in an analytical order. Fortunately, there is a wealth of reliable knowledge available in books, films and internet sites. Sifting through what historically occurred leading up to, during and after the battle is time-consuming. Then there’s the task of researching the Sun Dance ceremony, and what psychological/physiological impact it really had.
Organizing This Book
To make sense of what happened at the Battle of the Little Bighorn and the implications it still has on the Native American people, it’s necessary to look at this thing in bite-sized chunks. I’ve laid this book out accordingly. You can take any section and read it independently of other parts. Or, you can follow the book chronologically from section to section.
It’s not intended to produce a complete history lesson on Euro-American and Native American relations. Rather, this book is primarily about what caused the Little Bighorn battle, why Custer lost, and what happened afterward to result in the current Native American plight. It’s a case of not knowing where you are—and where you’re going—without knowing where you’ve been. Here’s how this book is organized:
This book is meant as a resource for students of the Battle of the Little Bighorn and to inform anyone interested in this historical milestone to clearly grasp the facts. It’s also meant to raise awareness of the rich and complex cultural contribution that Native Americans have to offer. As well, it’s to help understand the plight suffered by current Native Americans.
I try not to be a Custer apologist or to overly bash him. History has done its fair share of both. This is simply an attempt to get the truth—as best as possible.
 But, what I don’t think history has properly done is taking a detailed and objective look at the root cause of why Custer really lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn. And I’m sure nothing was more influential on how the battle turned out than the Sun Dance. I’m also positive George Custer never considered it.
But, what I don’t think history has properly done is taking a detailed and objective look at the root cause of why Custer really lost the Battle of the Little Bighorn. And I’m sure nothing was more influential on how the battle turned out than the Sun Dance. I’m also positive George Custer never considered it.
As much as Custer had over a decade of soldier experience—some of it on the plains—he had little or no appreciation of the Native American resolve to fight at the Little Bighorn. He also had no understanding of the Sun Dance culture and the mental effect it had on the Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne warriors. And Custer certainly had no idea how strong Sitting Bull’s spiritual guidance truly was.