Sixty years ago, on November 22nd, 1963, United States President John Fitzgerald Kennedy was shot dead while riding in his open limousine through Dallas, Texas. Within hours, Lee Harvey Oswald was captured and charged with President Kennedy’s murder. Oswald was never tried as he, too, was murdered—in the basement of the Dallas City Police building of all places. Officially, Oswald was the lone gunman. However, to this day, many people don’t believe that and are convinced there was a conspiracy to assassinate JFK.
Sixty years ago, on November 22nd, 1963, United States President John Fitzgerald Kennedy was shot dead while riding in his open limousine through Dallas, Texas. Within hours, Lee Harvey Oswald was captured and charged with President Kennedy’s murder. Oswald was never tried as he, too, was murdered—in the basement of the Dallas City Police building of all places. Officially, Oswald was the lone gunman. However, to this day, many people don’t believe that and are convinced there was a conspiracy to assassinate JFK.
Over my fifty years of being a serious student of the JFK Assassination, I‘ve dissected the investigation with a lot of folks. Some were sensible. Some were delusional. But the number-one person (in my opinion) who has the most in-depth knowledge of the Kennedy Assassination case facts is Scott Maudsley. Scott is here today for a discussion on the JFK file, so sit back and follow our thread. You might find it revealing.
Garry — Nice having you captive in the Dyingwords shack, Scott. We’ve been online and onphone friends for a long time, and it’s fitting you’re here for a JFK Assassination talk seeing as the 60th anniversary is upon us. To start, tell us about yourself and why does Jack Kennedy’s murder still captivate people’s interest?
Scott — Thanks for having me Garry. You flatter me. I’d say you are more knowledgeable about this case then I.
I’m 39 years old and a Toronto native. I have an honors BA in international development studies and currently work in security. I have a lifelong interest in history and politics and have been studying the JFK assassination since I was a child.
My chest is adorned with two large tattoos. One depicts the Titanic at the moment of collision with the iceberg, and the other depicts President Kennedy’s motorcade at the moment of the first shot. These are the events I’ve have spent my entire life studying.

Someone once said trauma is the closest thing we as humans have to time travel. Because when we think of traumatic events in our life, part of us is still trapped in that moment and always will be. We can often recall these moments in vivid detail.
I think moments in history, like the sinking of the Titanic or the assassination of JFK, endure in our collective minds because they’re an example of shared trauma that everyone experienced in the same way at the same moment.
Everyone who was alive to experience these events can recall exactly where they were and what they were doing when they first heard the news. Because it was so traumatic.
Garry — Intriguing perspective, Scott. I was seven years old when JFK was killed, and I remember the moment like yesterday. You weren’t born then, and it affects you today. But both of us weren’t a gleam in our grandparents’ eyes when the Titanic sank. How do these impersonal moments become imbedded in our inquisitive psyche?
Scott — It’s the cultural echoes of those events that stay with us. The idea of the unthinkable happening. These events can serve as a warning from history to not get too comfortable because life can change in sudden and unexpected ways.
So profound were the cultural echoes of both the Titanic and JFK assassination that they are still with us today, generations later. The discussion of the JFK case endures because of the supposed elements of mystery. People like a good whodunit.
Garry — Memento Mori.
Scott — Lol! Yes, exactly. I once read a book entitled The Dark Side of Camelot. In it, the author interviewed a woman who had a relationship with Kennedy. She said the lesson of the story of his life is that a person can live a privileged life and still meet an unexpected end.
John Jacob Astor was one of the richest men in the world. But none of that mattered when the ship he was on hit an iceberg in the middle of the night.
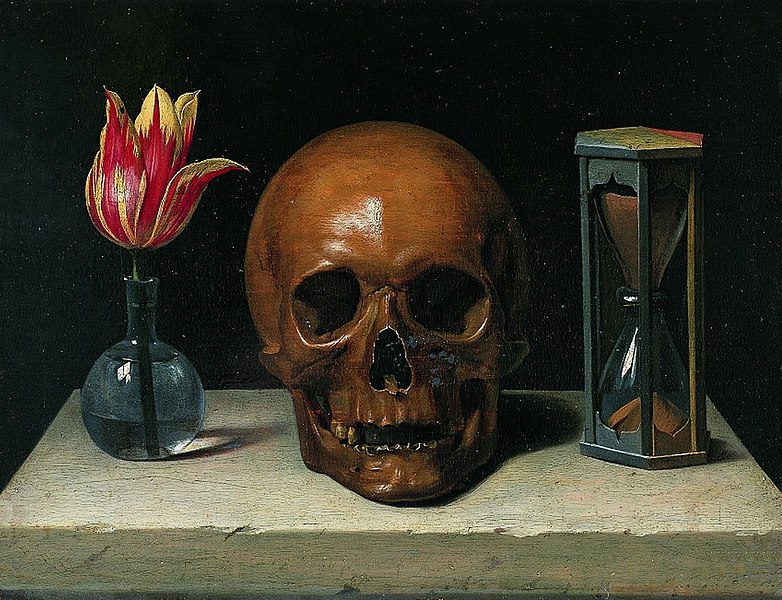

(Memento Mori – Tulip: Life, Skull: Death, Hourglass: Time)
Garry — Goes to show you… kings or billionaires… they’re all mortal and can leave this life at any time. Okay, let’s get into the case facts. If you had to present your evidence to prove your belief that Lee Harvey Oswald acted alone in murdering John Fitzgerald Kennedy, what would your irrefutable points be?
Scott — I would simply point to Oswald being at the scene of the crime, lack of alibi for the time of the shooting, an eyewitness seeing him shoot, and the weapon used in the shooting belonging to him.
Garry — For you and me who have seriously researched this case, it’s no mystery. The evidence that Oswald acted alone is overwhelming when you weigh the credible information. That and the fact there’s absolutely no credible evidence to indicate anyone else was involved. As they say, non events leave no evidence. But to so many people, the JFK case is still a whodunit. Why is that?
Scott — I think people see what they want to see and believe what they want to believe. If this case is still unsolved, in their minds, then there’s something more to be investigated and understood. There are still guilty people to be punished.
But, the truth is this case was solved within the first 48 hours of it occurring, as most murders are.
That does not satisfy some people. The killer was quickly caught and killed himself so in this way justice was denied and people never really got to have closure insofar as the concept of closure is a real thing that actually exists.
Garry — Yes, closure. For some, this case will never be closed because, deep down, they don’t want it to be closed. I think it’s very hard for some to accept that the All-American Boogeyman—the lowly, lone nut from a tall building with a cheap rifle—a crazy who took his gun to work and shot his boss—killed the highest person in the land. A king cannot be struck down by a peasant.
And as for the simplicity of the case, here’s a quote from Chief Justice Earl Warren, head of the Warren Commission investigating the Kennedy Assassination, “I have no hesitation in saying that had it not been for the prominence of the victim, the case against Oswald could have been tried in two or three days with little likelihood of any but one result.” Moving on, let’s talk about the forensic evidence—the body and the ballistics. How strong do you believe the scientific evidence is?

Scott — The thing about the JFK case is that everything is in dispute, and nothing is universally accepted by all sides. I believe the scientific and ballistic evidence is very strong. The fact that the projectiles recovered match the firearm recovered is very strong confirming evidence.
Garry — Playing the Devil’s Advocate, Scott, can you make a case that supports the conspiracy theory crowd? How is this thinking justified?
Scott — I’ve found that conspiracy theorists, or CTs for short, often are simply not familiar with the facts of the case, or they get these facts through secondary sources that distort what the primary source actually says. It’s from these flawed or incorrect interpretations that conspiracy theories arise.
One issue would be the failed attempt to probe the back wound during the autopsy. CTs point to that as being proof that the back wound was shallow and that the projectile did not fully transit JFK’s body, which is incorrect.
Garry — Let’s talk about the autopsy. In murder cases, the body is considered the best evidence. Setting aside David Lifton’s book Best Evidence where he proposed the ridiculous theory that Kennedy’s body was surgically altered prior to the Bethesda postmortem to reverse the proof of the shot directions (support a Grassy Knoll shooter), there are some issues with the autopsy that led to later interpretation problems.
Regarding the back wound, probing was difficult due to the narrow 6.5 mm passageway that closed up—caused by rigor mortis and stiffening of the strap muscles. Also, they failed to identify the throat exit wound which had mostly been obliterated by the tracheotomy incision made during life saving efforts. Plus, the pathologists used two movable reference points as markers to locate the back’s entrance wound. Other than that, do you think the autopsy was accurate or was it in “bungled” as some say?
Scott — It was for sure accurate, but the science of forensic pathology has undergone a lot of evolution in the last 60 years so it’s not as accurate as modern people expect it to be. The so-called CSI effect.
None of the doctors who performed the autopsy were unqualified or incompetent in any way.
It’s interesting to note that while later investigations into the medical evidence might have been critical of the conduct of the autopsy, none of them disagreed with the fundamental conclusions. That the President was killed as a result of 2 projectiles both fired from above and behind.
Garry — I’ll go a step further, having a lot of experience in firearms. So many CTs don’t accept that all shots were fired from the rear. Especially the head shot so famously distorted from Oliver Stone’s movie JFK where Kevin Costner’s character repeatedly drills home “proof” of the fatal shot being fired from the front. “Back and to the left. Back and to the left. Back and to the left.”
The infamous Frame 313 in the Zapruder film is a classic example of Newtonian physics in play — “For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.” It’s 100 % proof the fatal head shot was fired from Kennedy’s rear.
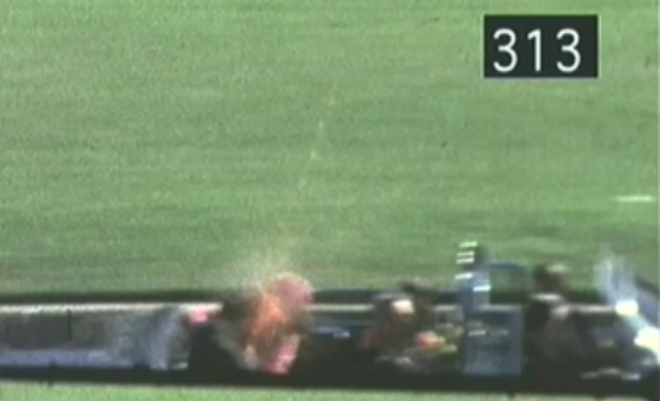

One time at an Emergency Response Team practice (I was the team’s trained marksman, sharpshooter, sniper, or whatever label you want to stick on my gunslinging back.), the guys got into a debate over the Kennedy fatal bullet direction. I went and got some melons and placed them 265 feet downrange which is the distance from Lee Harvey Oswald’s muzzle to JFK’s head when it exploded. I then shot the melons with a 5.56 and a 7.62. On every occasion when the melon exploded, the debris blew backward toward the bullet’s discharge point. Not forward.
Another thing regarding the brain matter blowing back and to the left which is so blatant in Zapruder 313 and 314. The limousine was moving forward at 11 mph into a 25-mph headwind. That’s a combined air movement force of a 36-mph frontal wind. It’s no wonder the mess went rearward and into that poor motorcycle cop’s face who was back and to the left.
Scott — Yes. There are many factors that led to the backwards motion of the head after the final shot. But it’s not because the shot originated from the front as most people suspect when viewing the Zapruder film.
Garry — I’ll bring up another elephant in the CT room. The police Dictabelt recording that allegedly proves four shots were fired, not three. What’s this all about? Go into detail here as this is what the 1978 House Select Committee on Assassinations (HSCA) review shamefully hung their hat on when they wrongfully concluded that JFK “was probably assassinated as the result of a conspiracy”.

Scott — So what happened, there was a police motorcycle parked at the Dallas Trade Mart (Kennedy’s destination) with a stuck microphone which was constantly recording. The motorcycle backfired, and this was interpreted as a gunshot. Something important to note is the quality of the audio in this recording is not great. The original audio was recorded using a simple blunt stylist and a rotating wax drum.
The HSCA report totally supported the conclusions of the original investigations, but at the 11th hour this audio evidence and an incorrect interpretation of it (the backfire recorded on a separate channel) was inserted into the final version of the report saying that the audio evidence indicated a possible 4th shot and thus a probable conspiracy.
However, the HSCA report also concluded that this possible 4th shot failed to hit anything or anyone. So right away this caused a stir, and the issue was taken up by the National Academy of Sciences in the United States.
Their investigation concluded that what had been interpreted as a gunshot on the audio recording had actually been recorded after the shooting and therefore could not have actually been gunfire.
In 2013, Professor Larry J. Sabato, Ph.D. commissioned a study on the Dictabelt recording using more modern analytical techniques. The report concluded that the recording did not contain sounds of the assassination gunfire and that it would be of “doubtful utility” as evidence to prove or disprove a conspiracy.
The presence of background noise of an idling engine and doppler shifting of the sound of sirens passing the microphone made during the recording prove the motorcycle with the stuck microphone was actually stationary at the Trade Mart (when the recording was made).
So, the audio evidence is nothing more then a red herring. One that got a lot of people excited but unfortunately proved of no evidentiary value.
Garry — Okay, so it’s conclusive that three shots were fired, not four. All from the 6.5 mm Mannlicher-Carcano rifle that, conclusively, Oswald owned and used that day from the 6th floor window of the Dallas School Book Depository building. Go through each of them and describe what happened to the bullets.

Scott — The first shot was a little early. Oswald might have seen the branch of a tree creeping into his sight profile and fired early. This shot missed and we are not entirely sure what happened to it exactly.
One eyewitness later reported seeing a spark on the road behind the President’s limo as it passed. He thought that someone had thrown a firecracker at the parade, but I believe that what he saw was the projectile hitting the pavement and either disintegrating on impact or ricocheting somewhere and was never to be recovered.
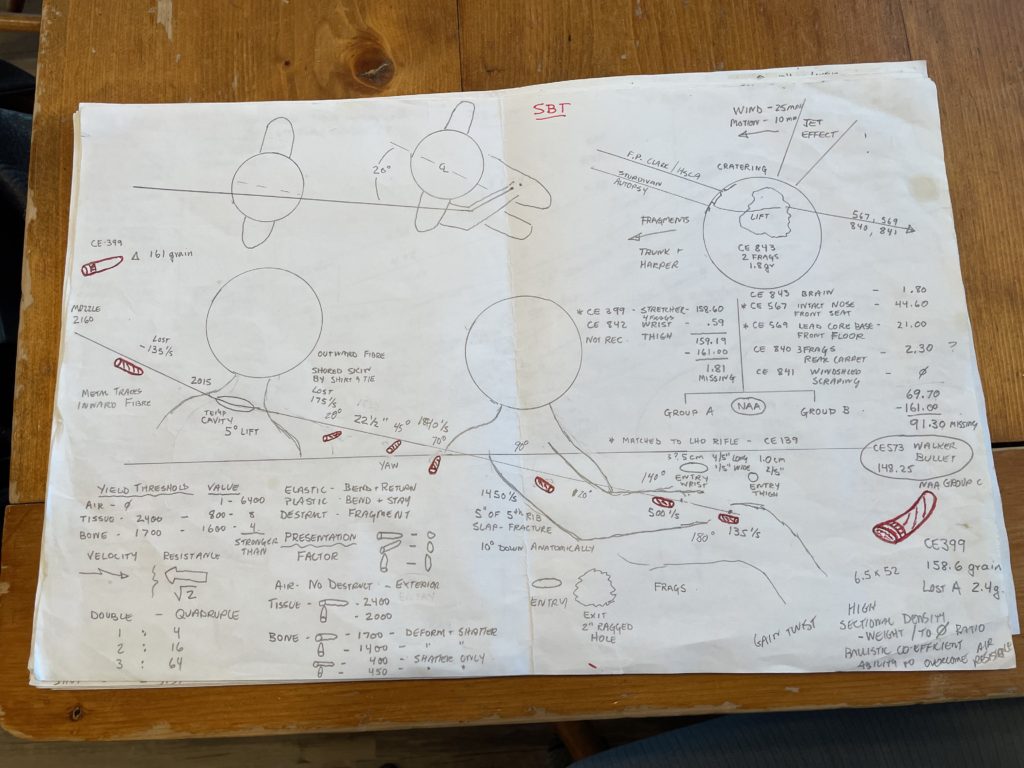
The second shot was the much-vaunted magic bullet, or Commission Exhibit (CE) 399, so called because of its relatively undamaged appearance. This projectile hit JFK in the upper back and passed through his neck without making any bony contact.
Once out in the open air, the projectile began to tumble and when it went into Governor Connally it was flying sideways.
Once it passed through the governor’s chest breaking ribs and collapsing a lung, it exited out, still tumbling, and passed though his wrist breaking the radius bone and ended up in his thigh, just having enough energy to break the skin and embed in a shallow wound from which it later fell out and was recovered from a stretcher in Parkland hospital.
The 3rd shot hit JFK in the back of his head and exited out the top of the head above the right eye. This projectile hit a chrome strip above the windshield and possibly the windshield itself before breaking into a nose and tail section which were recovered from the floor of the front passenger seat of the vehicle.
Garry — I think one of, if not THE, most misunderstood issues in the JFK Assassination is the “Magic” bullet (CE399). Most folks can’t accept that this bullet passed through the mass of two men and came out in a fired but “pristine” condition. There’s no question it was fired from Oswald’s rifle which was found stashed on the 6th floor, but the CT stance is that bullet had to be planted at the Dallas hospital. I’ve spent a lot of time researching this issue, and a few years ago I published a detailed explanation for how CE399 behaved to end up in this semi-intact and somewhat flattened state. For any readers who are interested in the mechanics, here’s a photo of my notes and the link to my post:
https://dyingwords.net/the-magic-bullet-in-the-jfk-assassination/
As for the missing bullet—the first shot—I also did a piece proposing that it hit the metal arm of a traffic light and was deflected. Here’s the notes and web link to that post.
https://dyingwords.net/missing-bullet-jfk-assassination/
Now having done some shameless self-promotion, let’s talk about the timing involved in the shot sequences. Another misconception is that all three shots were fired within six seconds, and there is no possible way anyone could accurately operate a bolt-action rifle like the Carcano in that amount of time. You have an identical rifle. What’s your take on the shot timing? Is this possible?
Scott — The original report gave some time frames for the total amount of time available for Oswald to have fired the shots based on which of the 3 shots was the one that missed. If, as we believe, it was the first shot that missed, then the time frame for the shooting extends to 8 to 12 seconds.
But even the low-end estimate of 6.5 seconds is still totally possible. I have let people shoot my rifle which is an exact copy of Oswald’s and with no experience with it, they have been able to get off 3 shots in about six seconds.
Garry — So this “can’t be done in six seconds” theory from CT books like Six Seconds in Dallas is rubbish?
Scott — Right. It’s nonsense.
Accuracy and experience with the rifle matter. But it is physically possible to fire 3 shots in that time frame. There are videos on YouTube of people doing it and I have personally seen people do it on my rifle.
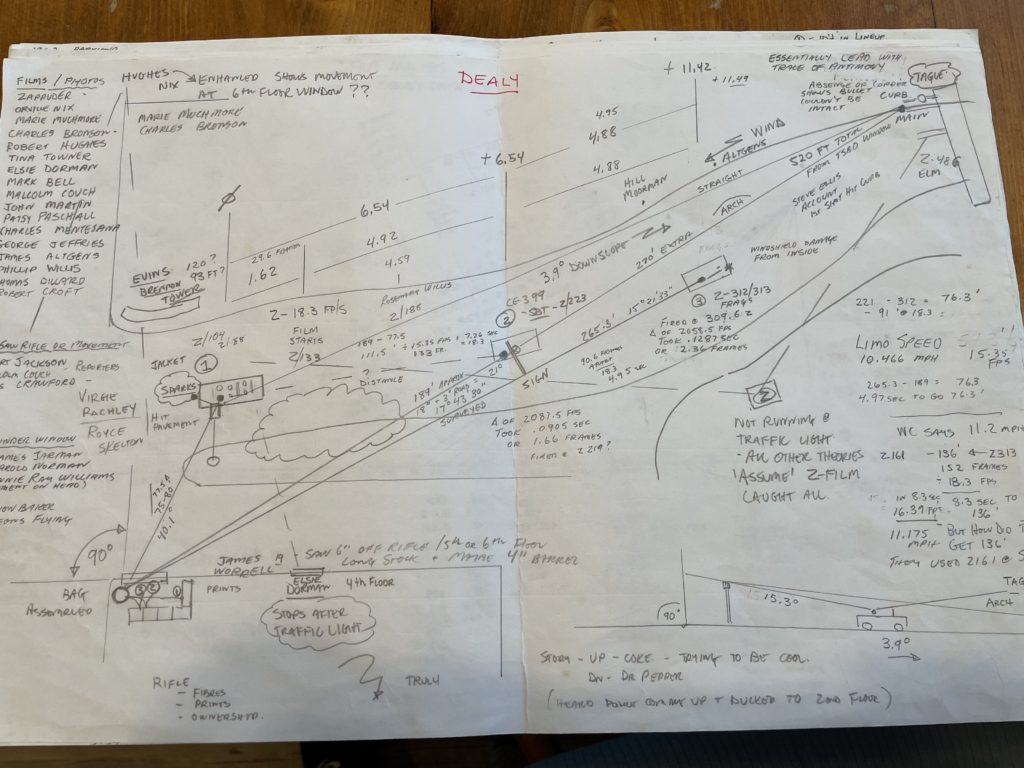
Garry — At one point in my JFK deep dive, I extrapolated information from reference points documented in a legal survey done of Dealy Plaza for the Warren Commission and correlated them to frames in the Zapruder film. Here’s a photo of the notes along with what I worked out:
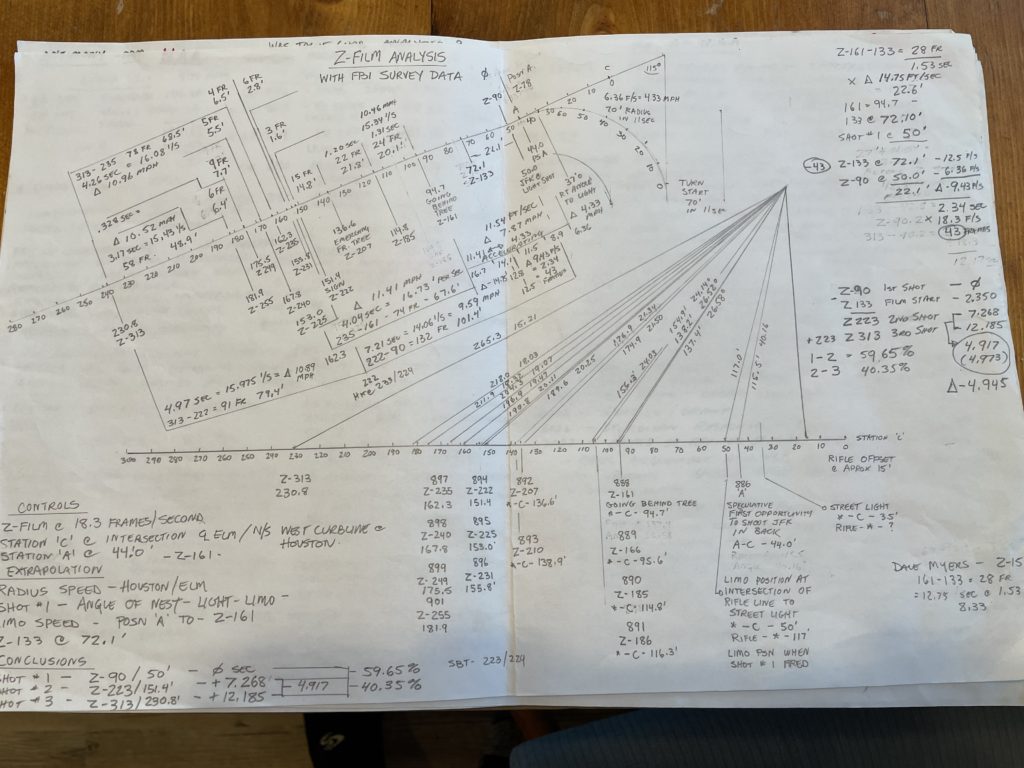
The first shot was fired at (Time) T-0:00, and it was 1:62 seconds before the Zapruder film started. The second shot hit JFK in the back at Zapruder Film Frame 223. Its impact was at T-6:54 or 6.54 seconds after the first shot was fired. The head shot struck at Zapruder Frame 312 and explodes at 313. It was at T-11.42 or 11.42 seconds after the initial shot’s discharge. That’s a lot of time to fire what works out to be two shots, not including the first one.
Respectively, the distances from Oswald’s barrel to the back shot at Z-223 was 189 feet, and from the barrel to the head shot at Z-312 was 265 feet. For someone shooting a rifle from a rest station, as Oswald had built in the “Sniper’s Nest”,’ that’s not very far or difficult at all. Also, the limousine was moving directly away from Oswald’s sight picture at shots 2 & 3, whereas during the first shot (the one I believe hit the traffic light arm) the limo was moving across Oswald’s sight picture from his left to his right.
I calculated that distance to be between 75 and 80 feet. It was a tough shot where Oswald was looking sharply down and moving sideways, aiming at a close-in, mobile target. Even if the bullet wasn’t deflected, it might have simply missed and struck the pavement. But, I doubt that, as the limo with JFK in it was a huge platform and Oswald would have to have been way, way off his shot picture to miss this target—which he sure wasn’t in the following shots.
The second shot had a bit of vision issue from the tree branches, but the third was wide open making Kennedy a sitting duck.
Moving on from the ballistics and other forensics, let’s talk about Oswald’s escape from the Book Depository and his capture at the Texas Theatre. Walk the audience through what happened.
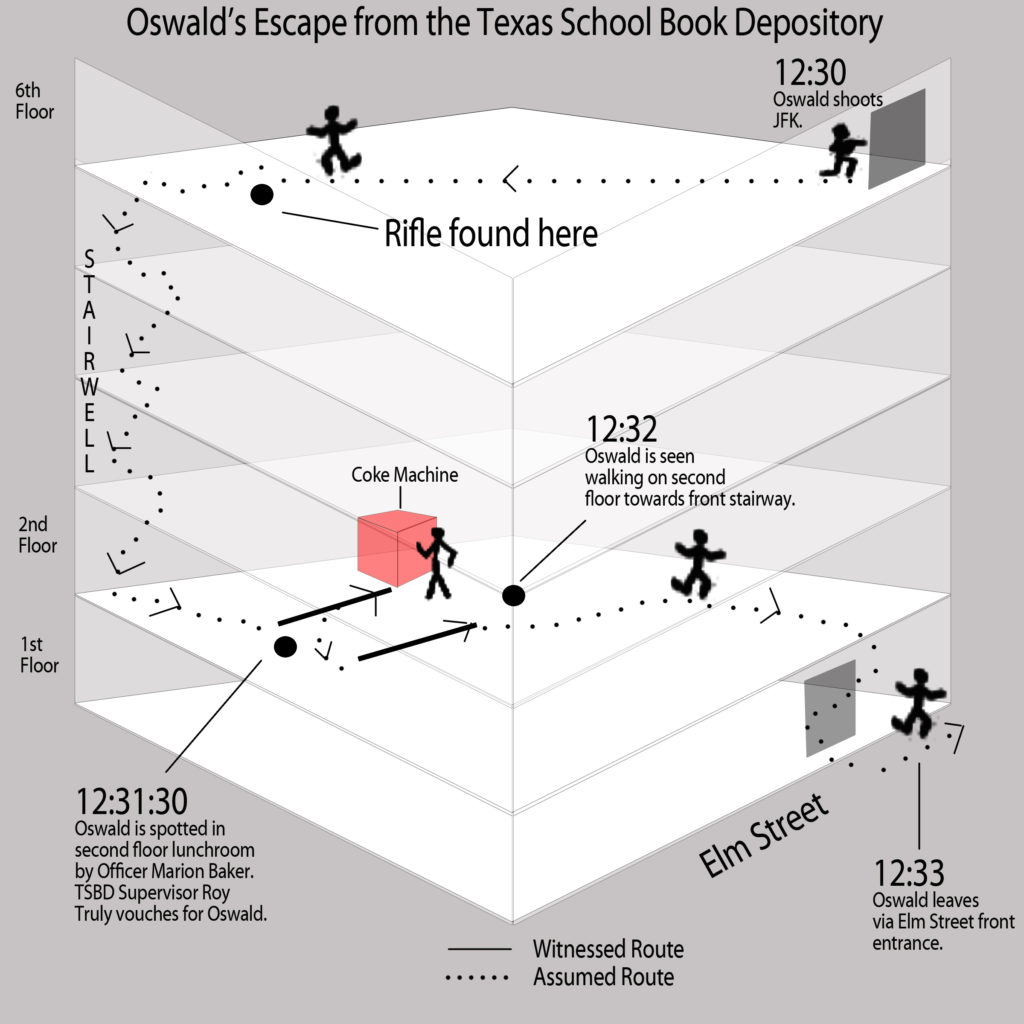
Scott — Oswald left the Sniper’s Nest on the 6th floor and descended the stairs to the 2nd floor. There he encountered the building manager and a police officer. The manager identified Oswald as an employee, the police officer dismissed him, and Oswald left the building through the front door, possibly giving directions to a pay phone to an AP reporter.
From there, he walked up the street to a bus that was stopped in traffic. He pounded on the door to get in, however, the bus was caught in traffic with the roads closed for the parade and was not moving. So, Oswald took a transfer and left. In an ironic turn of events, an old landlady of his was on the same bus and recognized him.
After leaving the bus, he walked a couple of blocks and got into a cab back to his rooming house. There he got his revolver and began walking. We don’t know where he was going or if he even had an intended destination.
He encountered Officer JD Tippit at a four-way intersection in a residential area, had a brief interaction with him, and then shot and killed the officer. Multiple eyewitnesses saw him either shoot the officer or being in the immediate aftermath with the gun still in his hands.
He gets away from the scene of the shooting but is spotted by an attentive shoe store worker who sees him duck into the store’s vestibule when some police cars go by. This worker follows him down the street where he sees Oswald duck into a movie theater without paying and he tells the movie theater attendant to call the police.
The police arrive and with the help of the shoe store worker identify and approach Oswald. He says, “This is it” and punches the officer closest to him. He also goes into his pocket and pulls out the revolver, but the arresting officer was quick and got his hand on it before Oswald had a chance to shoot.
Garry — If we think the evidence proving Oswald murdered President Kennedy is strong, the facts in the Officer JD Tippit case are airtight. Like eyewitnesses seeing him shoot Tippit, and then being caught with the murder weapon in his hand minutes later? Even if Oswald survived and beat the JFK murder charge, he certainly would have been convicted and sentenced to death for Tippit’s slaying.
Which brings me to Oswald not surviving. Jack Ruby? Like you couldn’t make someone like Ruby up. How in the hell did Ruby align with Oswald? Was this an incredible coincidence? What happened surrounding Jack Ruby being able to shoot and kill Lee Harvey Oswald?
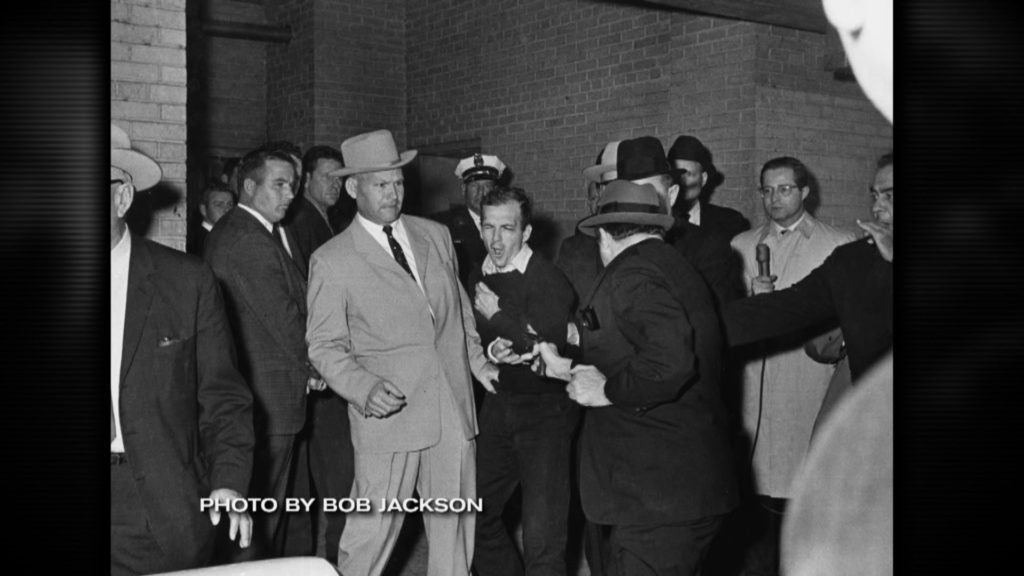

Scott — Jack Ruby was a local Dallas nightclub owner along with his sister who came from a family with a history of mental illness and institutionalization. His nickname was “Sparky” because of his short temper and willingness to get violent at the drop of a hat.
Ruby was on friendly terms with the local police who often frequented his clubs, and this friendliness offered him greater access to public figures. He spent the weekend hanging around police headquarters and even got close to Oswald on several occasions.
On Sunday, November 24th, Oswald was supposed to be transferred early in the morning but continued questioning by detectives and his own desire to change clothes delayed this until later in the morning.
One of Ruby’s employees called him, waking him up to ask for money. Oswald was already supposed to have been transferred to a more secure jail by then.
Jack Ruby got up, took his dogs, and went downtown to a Western Union office. There he waited in line and sent the employee some money before leaving and driving about a block to police headquarters where he saw a crowd gathered.
When a police officer stepped into the road to stop traffic to allow a vehicle to exit, Ruby slipped down the ramp undetected and shot Oswald when he walked out a few moments later.
Garry — So the contact between Ruby and Oswald was absolute fluke timing? Fate?
Scott — Yes. Something that could only happen in real life.
Garry — A lot has been made of Ruby being an underworld agent hired to take Oswald out, to silence him. And a lot has been made of Oswald being some sort of secret operative for a foreign government, given his travels to Russia and Mexico as well as his promotion of Cuba. What’s your understanding of this? Can you put Oswald’s past into some sort of sensible clarity?
Scott — Well, neither one of those things is true. Ruby might have rubbed shoulders with some underworld figures during his time in Chicago or simply by virtue of his owning a business that is active at night.
Garry — Ruby wasn’t a mob hitman.
Scott — No he wasn’t.
Oswald saw himself as a political person and sought to be politically active at least in his own way, so he would not hesitate to initiate contact with various government entities, but that was him acting on his own, he was never working for anyone and there is no proof of that claim whatsoever.
He saw himself as a political revolutionary of sorts. At a time when those ideas were gaining popularity in various parts of the world.
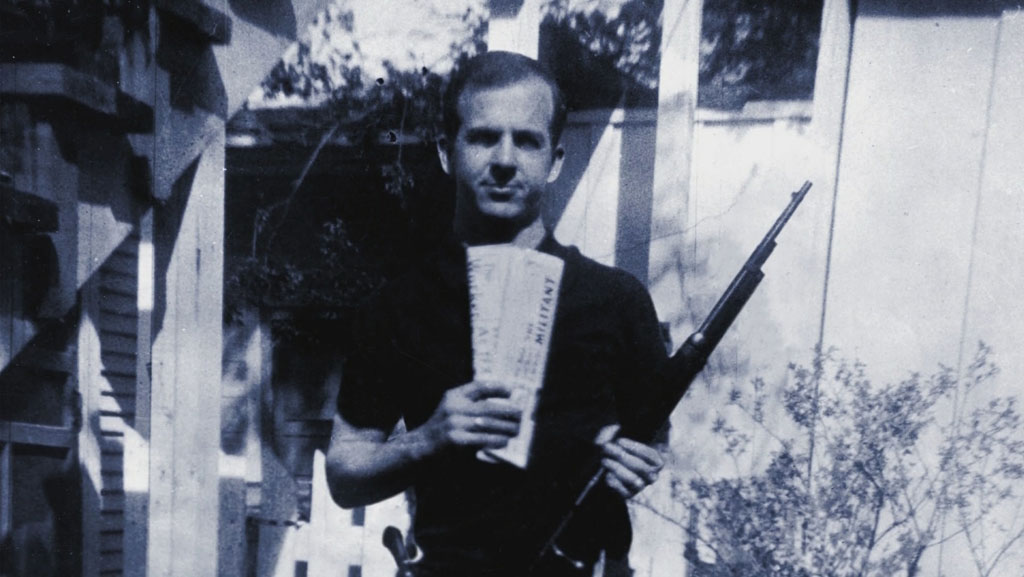

Garry — I think just an overview of Oswald is that he was a total loser. He had nothing that anyone would want—no secret, clandestine, or sinister entity needing him as fodder or setting him up as “a patsy” as he was quoted saying when he was paraded before the TV cameras at Dallas PD HQ. Never mind being so psychologically unstable. Like, who would recruit this guy?
Scott — Exactly. He was not a good candidate for intelligence work. Too emotional and unstable. He was completely unreliable and self-centered.
Garry — We’re wrapping up here, Scott. One thing I want to cover is the original United States Government investigation documented in the Report of the (President Johnson’s) Commission on the Assassination of President Kennedy chaired by Chief Justice Earl Warren, commonly known as the Warren Report. How accurate do you think it is? Has it stood the test of time?
Scott — Yes. 100%. Nothing in real life is ever perfect and although later investigations may have criticisms to make, all of them fundamentally get behind the conclusions of the Warren Report.
This case was solved long ago.
Really, it was solved within a couple of hours by the Dallas police.
Garry — Lone nut. Tall building. Cheap rifle. Opportunity chance of a lifetime. How was it that Kennedy and Oswald met in Dealy Plaza? Like the strands of fate?
Scott — To bring it full circle and invoke the memory of the Titanic again, someone once commented about the mix of ice and steel.
About all of the little factors that had to align in a certain way in order for those two things to be in the exact same place at the exact same time.
I think the JFK assassination is something similar, the mix of factors that had to align a certain way in order to produce an event like this.
Oswald was a malcontent. He was alienated from those around him and society to a more general extent.
He failed to get people to recognize his value as he saw it.
 He failed to get others to see him as he saw himself.
He failed to get others to see him as he saw himself.
His wife’s friend got him the interview for the job.
The job was hiring for multiple locations, he could have been hired for a location that was not on the parade route.
The parade route was selected because of the location of the luncheon. Which itself could have been held at a different location and thus would have had a different parade route.
It was raining that morning, it could have kept raining.
The mix of ice and steel.
Garry — Ice and steel. Great metaphor, Scott. There’s been countless books, articles, documentaries, blogs, pods, and whatever done about the Kennedy Assassination. Most are poorly reported and badly researched pieces of crap that promote any number of false conspiracy theories, some with incredibly stupid conclusions. I’ve read a lot of stuff, and I have five recommendations for anyone who really wants to know the facts—the truth—in the JFK murder case:
- The Warren Report
- Reclaiming History by Vincent Bugliosi
- The JFK Myths by Larry Sturdivan
- Case Closed by Gerald Posner
- The Death of a President by William Manchester
One important point in our JFK Assassination discussion is motive. Now, I have no idea what Oswald’s motivation was, and motivation is not an element needed to prove for a murder conviction. But, it’s important to cover or speculate upon for the average reader who would be left wondering “Why”.
Me? I think Oswald’s motive was something like Alfred said to Batman about The Joker in The Dark Knight, “Some men just want to watch the world burn.” What do you believe Oswald’s motive was for killing John F. Kennedy?
Scott — It’s always going to be difficult to assess a person’s individual motives for why they do anything. Oftentimes, they themselves don’t even really know.
Lee Oswald, in my opinion, was a violent person. He was violent as a child, in the Marine Corps, and in his marriage.
He attempted to make a place in history by doing something revolutionary and moving to the Soviet Union, but when he became disappointed in that he attempted to get into Cuba. When he failed at that, he attempted to assassinate a local right-wing political figure, and when he failed at that he plotted to assassinate Kennedy when he found out he’d have the ability to.
The night before he went to the house that his wife and children were staying in where his rifle was stored. He proposed the idea of getting a place in the city with his wife and children, but she resisted these advances much to her later regret. Unable to reconcile with his wife he took his rifle to work and performed that revolutionary act that got him the attention and recognition he always wanted.
So, it was a mix of personal, social, and psychological factors.
As all actions are.
Garry — Lastly, if we can tie this bundle up, what’s the legacy of the Kennedy Assassination? Why is this still important after sixty years?
Scott — You know, as I prepare for my 4th and final trip to Dallas next week, I’ve found myself asking the exact same question. I definitely think there’s a generational aspect to it. At 39, I’m often the youngest person at events in Dallas.
It’s a shared memory and a shared trauma. When the Oliver Stone movie came out, it was a revival moment and led to a resurgence of interest in the case. That’s how I personally came to have my interest, but even that was decades ago now.
The conspiracy theorist side of it is at least partly responsible for keeping the story alive. So, we could never have had the interest we do were it not for the conspiracy theorists who keep people interested as the years go by.
Had there never been a controversy about the case, it would have faded from memory long ago.
They go hand in hand. One could not exist without the other.
Garry — Great chatting with you, Scott. Safe trip my friend.
 There’s nearly unanimous agreement among historians that Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, was America’s greatest leader. Honest Abe, as he was affectionally called, served in the nation’s highest office from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. During that time of civil war, Lincoln’s guidance held the union together, and he worked towards the emancipation of slaves. But despite Lincoln’s reputation of calmness under stress, there was a dark side to him. Abraham Lincoln was known for his unpredictable fits of rage.
There’s nearly unanimous agreement among historians that Abraham Lincoln, the 16th President of the United States, was America’s greatest leader. Honest Abe, as he was affectionally called, served in the nation’s highest office from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. During that time of civil war, Lincoln’s guidance held the union together, and he worked towards the emancipation of slaves. But despite Lincoln’s reputation of calmness under stress, there was a dark side to him. Abraham Lincoln was known for his unpredictable fits of rage.