 Many crime writers mistakenly believe there’s a precise science to pronouncing time of death (TOD). There is a progressive process, but the sequence and time intervals are influenced by many factors. To craft convincing death scenes, authors need to know how a body actually breaks down.
Many crime writers mistakenly believe there’s a precise science to pronouncing time of death (TOD). There is a progressive process, but the sequence and time intervals are influenced by many factors. To craft convincing death scenes, authors need to know how a body actually breaks down.
Mortis is the anatomical term for changes in a body after the moment of death. Medically, that’s when the central nervous system gets unplugged and oxygenated blood is no longer delivered to the tissues, which naturally start recycling. The five types of mortis are:
-
Rigor – stiffening of muscles
-
Livor – settling of blood
-
Algor – change in temperature
-
Palor – change in color
-
Decomp – breakdown in tissue
 All these mortis conditions are integral to a decomposing process. Death is a part of life and decomposition is a part of death. Just as life is not always predictable, neither is estimating the post-mortem interval (PMI) between when death anatomically occurred and when first examination of the body begins.
All these mortis conditions are integral to a decomposing process. Death is a part of life and decomposition is a part of death. Just as life is not always predictable, neither is estimating the post-mortem interval (PMI) between when death anatomically occurred and when first examination of the body begins.
Death investigations work on a triangle of Body – Scene – History. It’s a holistic approach to determining cause of death (COD) and it’s the coroner’s responsibility to answer five universal questions:
-
Who is the deceased?
-
Where did they die?
-
When did they die?
-
What caused their death?
-
What was the means of death?
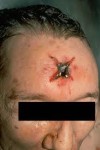 Some people are confused about the difference between cause and means. Cause is the medical reason. In this fellow’s case the cause of death would be traumatic brain injury. Means is the mechanism or physical reason – gunshot wound to the forehead.
Some people are confused about the difference between cause and means. Cause is the medical reason. In this fellow’s case the cause of death would be traumatic brain injury. Means is the mechanism or physical reason – gunshot wound to the forehead.
There can be thousands of causes of death, but there are only five classifications:
-
Natural
-
Accidental
-
Suicide
-
Homicide
-
Undetermined
 How this ties into mortis is that satisfying the five universal questions, great weight is placed on interpreting the body’s condition when first examined. This is where understanding the mortis process is so important and a lot of the interpretation comes from years of experience.
How this ties into mortis is that satisfying the five universal questions, great weight is placed on interpreting the body’s condition when first examined. This is where understanding the mortis process is so important and a lot of the interpretation comes from years of experience.
The proper pronunciation of the mortis states puts emphasis on the first syllable and it’s a long ‘I’ (RYE-gore).
Let’s look at each one.
Rigor Mortis is the stiffening of muscles. It’s caused by the body’s energy source, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), being depleted. With no energy left to keep the muscles flexible, they naturally go to a rigid state until another enzyme begins the breakdown of tissue and relaxation returns.
 Immediately upon death, the body enters a brief period of primary flaccidity where it’s dead limp. Depending on many factors, temperature and body mass being the big ones, the muscle stiffening begins in 1- 2 hours, first setting into the eyelids, jaw, and neck. It proceeds to the limb joints and extremities after 4-8 hours and fixes in the organs in about 12 hours. Rigor releases in a reverse sequence and can be absent in as little as 12 hours or can stay for days, again depending on factors.
Immediately upon death, the body enters a brief period of primary flaccidity where it’s dead limp. Depending on many factors, temperature and body mass being the big ones, the muscle stiffening begins in 1- 2 hours, first setting into the eyelids, jaw, and neck. It proceeds to the limb joints and extremities after 4-8 hours and fixes in the organs in about 12 hours. Rigor releases in a reverse sequence and can be absent in as little as 12 hours or can stay for days, again depending on factors.
Livor Mortis is the pooling of blood caused by gravitational settling once the heart stopped pressurizing the vascular system. It’s evident by purplish-red blotching where blood is free to pool and blanched-white where pressure points restrict it. Lividity, as it’s also known, sets in between 30 minutes to 1 hour after death and ‘fixes’ in about 8-12 hours. ‘Fixing’ is the entire settling where blood has coagulated and no longer runs free.
Algor Mortis is the change in body temperature. A cadaver will always achieve ambient temperature, regardless of time. A normal, living human’s core temperature is 36 Celsius (98.6 Fahrenheit) but the scene temperature could be anywhere above or below. In a cold environment, the body will drop to equilibriate. In a hot environment, it will rise. Here’s where so many peripheral factors come into play. Body size. Layered Clothing. Air movement. And the list goes on. A rule of thumb is that a body’s temperaature will change about 1 degree Celsius per hour.
 Palor Mortis is the change of color. Live humans are pretty much a reddish tinge due to oxygenated blood flowing (different tones for different races). Immediately upon death, a bluing phase occurs, following by a grey, then a white, and it can be a rainbow of colors as decomposition takes over.
Palor Mortis is the change of color. Live humans are pretty much a reddish tinge due to oxygenated blood flowing (different tones for different races). Immediately upon death, a bluing phase occurs, following by a grey, then a white, and it can be a rainbow of colors as decomposition takes over.
Decomp, or decomposition, is not really a true class of mortis – rather it’s the culmination of the four mortis processes which leads to a breakdown of the body tissues and a return to nature.
Decomposition is a complex and unpredictable thing. There are two processes that morph into one:
-
Putrefaction – action of bacteria on body tissues
-
Autolysis – body breakdown by endogenous substances
 In most deaths these two work in tandem, starting with a breakdown in internal organs which produces gas. This causes bloating and skin discoloring, as well as the foul odor from purging or ‘gassing-off’. As the muscle tissues change, the skin begins to dislodge, the joints become loose enough to disarticulate, fats become liquefied, and bones become exposed. Advanced decomp can become skeletonized, mummified, or consumed – again depending on so many factors, which all start from the mortis process.
In most deaths these two work in tandem, starting with a breakdown in internal organs which produces gas. This causes bloating and skin discoloring, as well as the foul odor from purging or ‘gassing-off’. As the muscle tissues change, the skin begins to dislodge, the joints become loose enough to disarticulate, fats become liquefied, and bones become exposed. Advanced decomp can become skeletonized, mummified, or consumed – again depending on so many factors, which all start from the mortis process.
