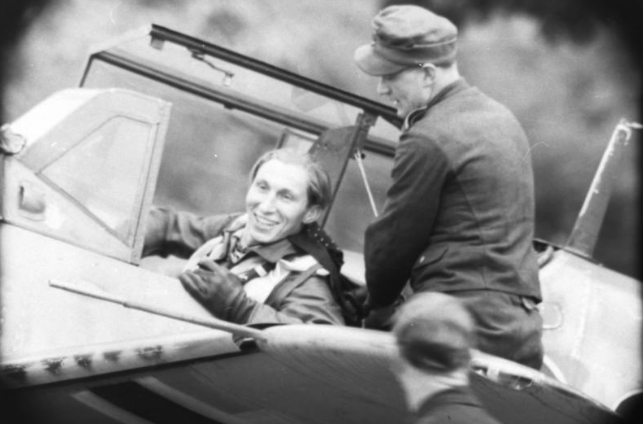
Let’s time-travel to 1940 and climb inside the cockpit of a German Air Force Messerschmitt Bf 109. The Luftwaffe pilot at the controls hasn’t slept in nearly three days. His pupils are dilated, his hands are steady, and his focus is razor sharp. He’s flying on more than av-gas and adrenaline—he’s flying on methamphetamine—speed as it’s commonly called on the street.
Let’s time-travel to 1940 and climb inside the cockpit of a German Air Force Messerschmitt Bf 109. The Luftwaffe pilot at the controls hasn’t slept in nearly three days. His pupils are dilated, his hands are steady, and his focus is razor sharp. He’s flying on more than av-gas and adrenaline—he’s flying on methamphetamine—speed as it’s commonly called on the street.
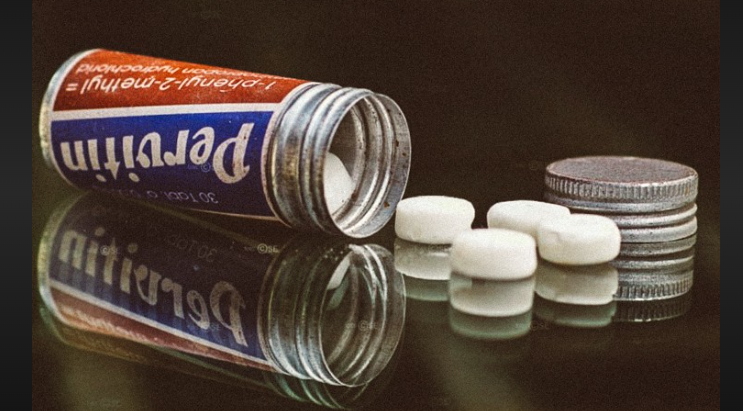
Pervitin, the brand name for methamphetamine or meth in Nazi Germany, wasn’t some top-secret wonder drug. It was mass-produced, passed around like breath mints, and handed out to Axis troops in the millions. This pharmaceutical stimulant, also known in a form called crystal meth or ice, fueled one of history’s most aggressive military machines. But it also left a wake of destruction, back in that war and now in our attempt at keeping peace on our modern-day streets.
What Exactly Is Methamphetamine?
Methamphetamine is a specific synthetic stimulant that belongs to a broader class of drugs known as amphetamines. Structurally, it’s like dopamine and norepinephrine—two neurotransmitters that play a key role in human motivation, attention, mood, and arousal.
When meth enters the bloodstream, it crosses the blood-brain barrier quickly. Inside the brain, it floods the synaptic clefts with dopamine, while also preventing its reuptake. This creates a chemical bottleneck—one that leads to an unnatural surge of euphoria, energy, and hyperfocus. Users feel confident, invincible, and tireless.
Physiologically, meth elevates heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. It suppresses appetite and overrides the body’s normal sleep cycle. Psychologically, it induces a profound sense of well-being—followed by devastating crashes, anxiety, paranoia, and hallucinations. Chronic use leads to neural toxicity and long-term damage to the brain’s dopamine system, contributing to psychosis, cognitive decline, and profound depression.
Pervitin, the methamphetamine compound dispensed to Nazi flyers and ground pounders, was particularly potent. Each tablet contained 3 mg of methamphetamine hydrochloride—roughly equivalent to a strong recreational dose today. Axis airmen were known to consume dozens over the course of a week.
Medical Madness: How Nazi Scientists Pushed the Limits
Dr. Otto Ranke, a military pharmacologist, was the architect behind Pervitin’s deployment in the Wehrmacht. He believed fatigue was the ultimate enemy and chemical warfare the ultimate answer. Under his guidance, military medics tested Pervitin in controlled experiments—monitoring heart rates, alertness levels, and combat performance in dosed vs. sober units.
In 1939, 35 million Pervitin tablets were sent to German soldiers in anticipation of the Blitzkrieg in Poland. In the 1940 France campaign, Nazi stormtroopers and tank crews blitzed hundreds of miles with no rest, thanks to constant dosing. Luftwaffe pilots flew long sorties with heightened aggression and tunnel-visioned intensity.
One extreme example involved Luftwaffe pilot Siegfried Hess, who reportedly flew over 40 hours with only brief breaks, fueled entirely by methamphetamine. After his mission, Hess collapsed and suffered a psychotic breakdown. He never flew again.
Pervitin in the Cockpit: Highs and Horrors
Speed gave Luftwaffe pilots an edge—short-term. They were more alert, less inhibited, and far more aggressive. Some described entering a kind of god-mode, where time slowed down and every decision felt intuitive.
But the chemical edge came at a severe cost. Sleep deprivation combined with meth-induced overdrive led to hallucinations, blackouts, and crash landings. One bomber pilot, Karl Lange, testified post-war that during a night mission over London, he hallucinated enemy planes attacking from above and opened fire on his own escort fighters.
Commanders initially praised such intensity. But as the war dragged on, they saw the consequences—fractured judgment, psychotic behavior, and moral detachment. Many pilots became erratic, insubordinate, or suicidal. By 1941, the Nazi command began curbing open distribution of Pervitin—but by then, addiction was widespread.
The Allies Jump In
The Allies were not immune to the chemical temptations of war. British troops were issued Benzedrine inhalers (another form of amphetamine), and the RAF distributed pills to bomber crews flying the deadly “round trip” missions over Europe.
The U.S. military adopted amphetamine use during the North African campaign and later in the Pacific Theater. One case involved American paratroopers in Operation Market Garden who reported taking Benzedrine before jumping behind enemy lines. They claimed the drug gave them courage, numbed pain, and kept them going when they otherwise would have collapsed.
Still, the Allied usage was more regulated. Unlike Nazi Germany, where drug use was institutionalized and systemic, the Allies saw amphetamines more as tactical aids—not ideological tools.
From War to Addiction: The Post-War Fallout
After the war, millions of Pervitin tablets remained in circulation. In Germany and Japan, they were sold illegally or hoarded by veterans. Addiction soared. Civilians, many suffering from post-war trauma and poverty, turned to meth as a coping mechanism.
One of the most telling stories came from Japan. Known as “Philopon,” meth was handed out to kamikaze pilots before missions. After the surrender, leftover supplies flooded the streets. By 1950, Japan faced its first meth epidemic—one so severe that special task forces were formed to combat widespread addiction and crime.
In the United States, pharmaceutical amphetamines became a staple of the 1950s and 60s counterculture. Truckers used them to stay awake. Students and housewives turned to them for weight loss and productivity. By the time the government recognized the public health crisis, millions were already hooked.
The Physiology of Long-Term Meth Use
Unlike cocaine or alcohol, meth causes lasting changes in brain chemistry. Repeated use shrinks gray matter, erodes dopamine receptors, and damages the prefrontal cortex—the seat of judgment and impulse control.
Heavy users often develop “meth mouth” due to dry mouth, grinding, and poor hygiene. Skin sores result from obsessive picking—a behavior linked to sensory hallucinations known as “formication,” or the sensation of bugs crawling under the skin. Chronic users show signs of schizophrenia, including auditory hallucinations, paranoia, and violent mood swings.
In one high-profile Canadian case, Vince Li, a diagnosed schizophrenic with a history of meth use, beheaded a fellow bus passenger in 2008 during a psychotic break. Although he was found not criminally responsible due to mental illness, his meth abuse was cited as a key aggravating factor in his psychiatric decline. (For more on this tragic case here’s a link to the DyingWords post titled The Guy on the Greyhound Bus.)
Modern Militaries and the Ongoing Legacy
Methamphetamine use didn’t end with WWII. U.S. forces used amphetamines in Vietnam and even the Gulf War. The term “go pills” persisted well into the 2000s, with Air Force pilots issued Dexedrine for long sorties.
One tragic case occurred in 2002, when two American F16 Viper pilots mistakenly bombed Canadian troops during a mission in Afghanistan. Investigations revealed they were on military-issue amphetamines, raising questions about impaired judgment and the blurred line between alertness and recklessness.
Today, military doctrine is shifting. Modern forces focus more on fatigue management, rotation schedules, and cognitive tech. Yet the echoes of Pervitin and its synthetic siblings still ripple through defense policy and medical ethics.
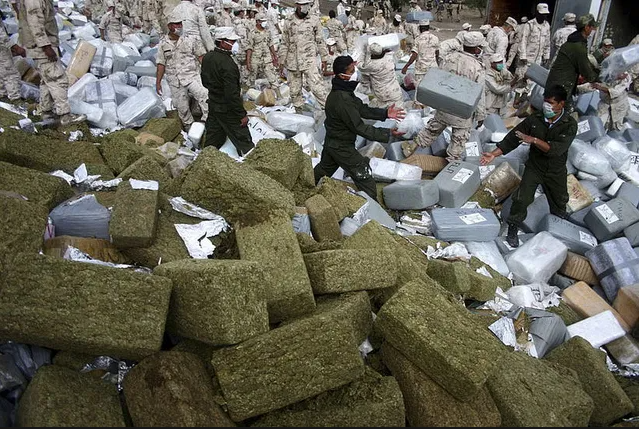
The Scourge in Society Today
Globally, methamphetamine is one of the most abused drugs. It’s cheap to make, easy to distribute, and devastating in effect. Entire towns have collapsed under the weight of meth-related crime and dysfunction.
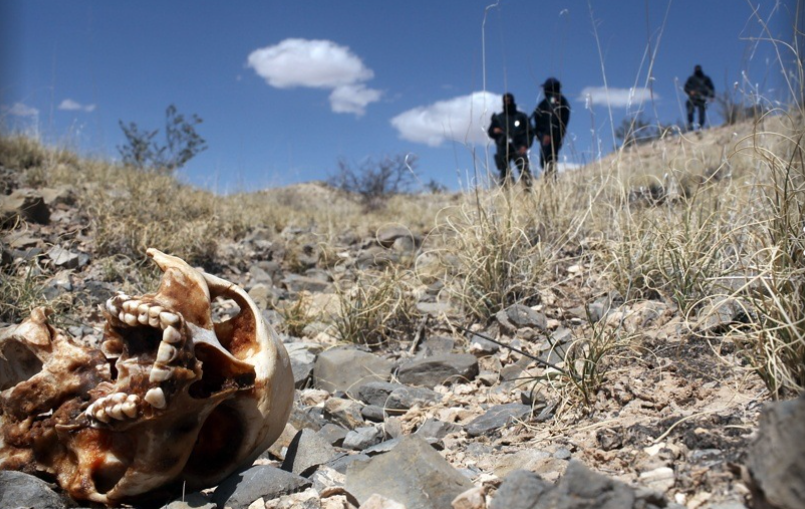
In British Columbia, my home province in Canada, meth use is linked to severe violence, prohibitively expensive property crime, uncontrolled gang activity, and deadly mental health crises. I’ve seen the toll firsthand on the street by my house—paranoid users attacking innocent strangers, psychotic events during arrests, and the heartbreak of families torn apart by addiction and overdose deaths.
Law enforcement and public health agencies try to work together to stem the tide. However, the socialist political system in British Columbia and its bizarre tolerance of drug abuse makes it nearly impossible to curtail the crisis. And sadly, the war on meth, like many wars, is far from over.
Thoughts from a Former Homicide Cop and Coroner
Pervitin was a military experiment in chemistry-fueled courage. In the end, it proved that no drug can shortcut the human condition. The Luftwaffe’s speed-fueled blitzkrieg bought Hitler early victories, but it also cracked the minds of his airmen—and laid the groundwork for one of the most addictive and destructive substances in human history.
As someone who’s looked into the eyes of meth addicts—both as a cop and a coroner—I’ll say this: meth doesn’t just ruin lives. It scrapes out the soul. It kills empathy. It reduces people to hollow shells, far darker than mere human husks.
So yes, Hitler’s Luftwaffe pilots were wired on speed. And we’re suffering the fallout today.