No movie star lived on after death like Marilyn Monroe. She was far more than a bleached-blonde bombshell with a voluptuous frame and a lusty voice—she intuitively knew her craft. Born in poverty as Norma Jean Mortenson (aka Baker) to a mentally unstable mother, Marilyn Monroe rose to Hollywood glamor, fame, and idolization beyond what few ever reach. Tragically, by the time she died at age thirty-six, her performing career had spiraled into the same abyss that her personal relationships and head space were already in.
No movie star lived on after death like Marilyn Monroe. She was far more than a bleached-blonde bombshell with a voluptuous frame and a lusty voice—she intuitively knew her craft. Born in poverty as Norma Jean Mortenson (aka Baker) to a mentally unstable mother, Marilyn Monroe rose to Hollywood glamor, fame, and idolization beyond what few ever reach. Tragically, by the time she died at age thirty-six, her performing career had spiraled into the same abyss that her personal relationships and head space were already in.
Marilyn Monroe was found dead in her Beverly Hills bed at 3 a.m. on Sunday, August 5, 1962. The scene (at the time) suggested nothing suspicious—no foul play or culpable act, that is—and the toxicology results from her autopsy proved she’d succumbed to a lethal dose of prescription drugs. The coroner ruled her death as “probable suicide” but, like the deaths of other uber-celebrities, many people mumbled murder. Monroe’s death was reinvestigated in 1992 by the Los Angeles District Attorney who came to the same conclusion — “probable suicide”.
“Probable” is not in the official vocabulary of today’s coroner-speak. Neither is “possibly”. Everywhere in the civilized world, coroners are mandated by legislation to rule classifications of death as being in one of five definite categories: Natural, Homicide, Accident, Suicide, or Undetermined. Now, nearly sixty years later, an impartial look at Monroe’s case facts indicate her death classification definitely was not natural and cannot conclusively be classed as an accident or a suicide.
Does that mean Marilyn Munroe’s death was actually a homicide?
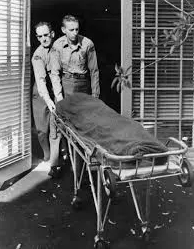 On the day of her death, many people were in Marilyn Monroe’s company. None reported any immediately implied threat or perceived action from Monroe that suggested an imminent danger of suicide, nor any behavior that was outside of her already troubled mental state of manic highs and depressive lows. She’d a history of emotional instability that, today, would likely be classified as Bipolar II Disorder, and she was under the continual care of a general physician and a psychiatrist. Monroe was no stranger to prescription pharmaceuticals, specifically anti-depressants and sleeping pills, but she was a relatively light alcohol drinker.
On the day of her death, many people were in Marilyn Monroe’s company. None reported any immediately implied threat or perceived action from Monroe that suggested an imminent danger of suicide, nor any behavior that was outside of her already troubled mental state of manic highs and depressive lows. She’d a history of emotional instability that, today, would likely be classified as Bipolar II Disorder, and she was under the continual care of a general physician and a psychiatrist. Monroe was no stranger to prescription pharmaceuticals, specifically anti-depressants and sleeping pills, but she was a relatively light alcohol drinker.
Marilyn Monroe had a difficult year in 1961. She worked very little due to health issues. Besides her emotional imbalance and substance dependency, she underwent surgery for endometriosis (uterus ailment) and a cholecystectomy (gall bladder removal), then suffered a painful attack of sinusitis. Her stress level soared from a lawsuit with 20th Century Fox where they sued Monroe for breach of contract—her erratic behavior led to delays in filming, disputes with cast and crew, then finally a stop of production.
On Saturday morning, August 4, Marilyn Monroe met with her official photographer and discussed an upcoming Playboy deal, then kept a massage appointment, a meeting with her publicist, talked with friends on the phone, and signed for deliveries for her house renovation. She was visited by her psychiatrist, Dr. Ralph Greenson, in the late afternoon for a scheduled therapy session. Greenson left around 7 p.m. and reported no alarming behavior, however he ensured that Monroe’s housekeeper, Eunice Murray, would be staying overnight.
Marilyn Monroe retired to her bedroom around 8 p.m. The last person to have contact with Monroe was actor Peter Lawford who invited her to a Hollywood party. He reported that in their phone conversation Monroe sounded tired—sleepy—as under the influence of drugs. After their call, Lawford became alarmed and phoned back to the house where he got Murray. She assured him everything was fine with Monroe.
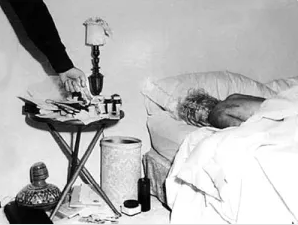 At 3 a.m. on Sunday morning, Eunice Murray woke and noticed light coming from under Monroe’s bedroom door. Sensing something not right, Murray tapped on the door. There was no response, so she tried the handle and found it locked, which she stated was unusual.
At 3 a.m. on Sunday morning, Eunice Murray woke and noticed light coming from under Monroe’s bedroom door. Sensing something not right, Murray tapped on the door. There was no response, so she tried the handle and found it locked, which she stated was unusual.
Now alarmed, Murray phoned Dr. Greenson who instructed her to go outside and look through the bedroom window. She did and observed Marilyn Monroe lying facedown on the bed, covered in a sheet, and clutching a telephone receiver in her right hand.
Greenson arrived at approximately 3:20 a.m., broke the window with a fireplace poker, and climbed in. Immediately, he could tell Monroe had been dead for some time and it was pointless to call an ambulance or attempt resuscitation. Greenson phoned Monroe’s physician, Dr. Hyman Engelberg, who arrived at around 3:50 a.m. Engelberg examined Monroe by removing the phone receiver and rolling her over, officially pronouncing death. At 4:25 a.m. they notified the LAPD.
The attending detective agreed with the two doctors that there was nothing to indicate foul play and the death was most likely a drug overdose. The detective photographed the scene and recorded the “pill count” of the pharmaceutical vials on Monroe’s nightstand. Dr. Engelberg noted a vial containing twenty-five capsules of the barbiturate Nembutal that he’d prescribed two days earlier was empty. Vials with other prescriptions appeared in order including one containing the sleeping sedative Chloral Hydrate.
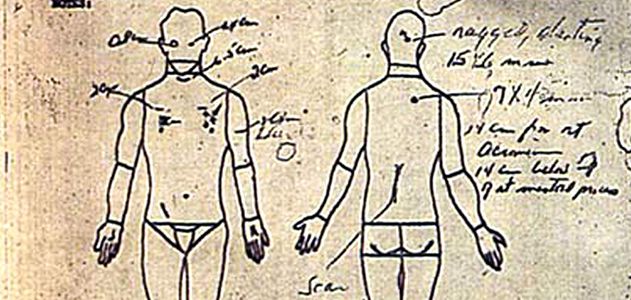
 Marilyn Monroe was autopsied on the morning of August 6 by pathologist Dr. Thomas Noguchi who would later be known as “Coroner To The Stars” for his many postmortem exams on celebrities. His original autopsy report for Marilyn Monroe is on the public record and can be downloaded.
Marilyn Monroe was autopsied on the morning of August 6 by pathologist Dr. Thomas Noguchi who would later be known as “Coroner To The Stars” for his many postmortem exams on celebrities. His original autopsy report for Marilyn Monroe is on the public record and can be downloaded.
Noguchi is very clear in his report, and in many subsequent interviews, that he found no evidence of physical trauma—specifically needle marks—on Monroe’s body. Based on his observations and those of Drs. Greenson and Engelberg regarding Monroe’s rigor, livor, algor, and palor mortis conditions, he felt reasonable to estimate her time of death between 8 and no later than 10 p.m. the previous night. Noguchi found no natural cause of death and waited for the toxicology report before forming his final conclusions.
The tox screen was done by the LA County Coroner’s laboratory and released on August 13. The results concluded Monroe’s blood contained 4.5 milligrams (percent) of Nembutal and 8.0 milligrams (percent) of Chloral Hydrate. Her liver contained 13.0 milligrams (percent) of Pentobarbital. Blood ethanol (alcohol) was absent.
Noguchi was satisfied the combination of Nembutal and Chloral Hydrate levels in Monroe was sufficiently high to cause her death through respiratory and central nervous system failure and he knew the Pentobarbital stored in her liver was simply indicative of someone who had long exposure to barbiturates and developed a “tolerance”. Noguchi certified the cause as “acute barbiturate poisoning due to ingestion of overdose” but he was reluctant to rule the classification as “suicide”. Though Noguchi was certain no evidence existed to suggest the death was an intentional homicide, he was uncomfortable with there being no clear evidence that Monroe intended to take her own life.
There were no immediate threats, no suicide note, no warning behavior, and not all the Chloral Hydrate pills were consumed, not like the Nembutal.
It might be an accidental OD, Noguchi thought, and he was troubled by the fact Monroe had been prescribed the amounts of Nembutal and Chloral Hydrate at the same time—her physician had to have known they’d be lethal if mixed a large quantity.
Noguchi was under pressure—political pressure, if you will—from the elected Chief Coroner of Los Angeles County to shut down media speculation that there might be more to Monroe’s death than a sad case of a despondent star intentionally extinguishing her light. The Chief and Noguchi reached a temporary compromise that they’d say Monroe’s death was a “probable” suicide.
Noguchi didn’t go so far as to insinuate negligence by Monroe’s caregivers might be the smoking gun, yet he requested a “psychological autopsy” to investigate Marilyn Monroe’s mental state leading to her death. Without clear evidence of an intentional suicide, the pattern of Monroe’s behavior was crucial in corroborating a suicide rule.
This statement was issued by LA County Chief Coroner Theodore J. Curphey. It’s an addendum to Noguchi’s final autopsy report:
“Following is the summary report by the Psychiatric Investigative Team which assisted me in collecting information in this case. The team was headed by Robert Litman, M.D., Norman Farberow. Ph. D., and Norman Tabachnick, M.D.:
‘Marilyn Monroe died on the night of August 4th or the early morning of August 5th, 1962. Examination by the toxicology laboratory indicates that death was due to a self-administered overdose of sedative drugs. We have been asked, as consultants, to examine the life situation of the deceased and to give an opinion of the intent of Miss Monroe when she ingested the sedative drugs which caused her death. From the data obtained, the following points are the most important and relevant:
Miss Monroe suffered from psychiatric disturbance for a long time. She experienced severe fears and frequent depressions. Mood changes were abrupt and unpredictable. Among symptoms of disorganization, sleep disturbance was prominent, for which she had been taking sedative drugs for many years. She was thus familiar with and experienced in the use of sedative drugs and well aware of their dangers.
Recently, one of the main objectives of her psychiatric treatment had been the reduction of her intake of drugs. This has been partly successful during the last two months. She was reported to be following doctor’s orders in her use of drugs; and the amount of drugs found in her home at the time of her death was not unusual.
In our investigation, we have learned that Miss Monroe had often expressed wishes to give up, to withdraw, and even to die. On more than one occasion in the past, when disappointed and depressed, she made a suicide attempt using sedative drugs. On these occasions, she had called for help and had been rescued.
From the information collected about the events on the evening of August 4th, it is our opinion that the same pattern was repeated except for the rescue. It has been our practice with similar information collected in other cases in the past to recommend a certification for such deaths as a probable suicide.
Additional clues for suicide provided by the physical evidence are:
(1) the high level of barbiturates and chloral hydrate in the blood, which, with other evidence from the autopsy, indicate the probable ingestion of a large amount of drugs in a short period of time;
(2) the completely empty bottle of Nembutal, the prescription for which was filled the day before the ingestion of drugs; and
(3) the locked door which was unusual.’
Now that the final toxicological report and that of the psychiatric consultants have been received and considered, it is my conclusion that the death of Marilyn Monroe was caused by a self-administered overdose of sedative drugs and that the mode of death is probable suicide.
– Theodore J. Curphey, M.D. Chief Medical Examiner-Coroner for the County of Los Angeles, August 13, 1962.”
There’s that word “probable” again.
In my time as a police officer and coroner, I’ve attended many drug overdose deaths. Some were clearly suicides, backed-up by recorded threats and present notes. Some were accidents by misadventure, usually mixed with alcohol. And some were undetermined—not shown to have a definite intent by the decedent to take their own life.
I’d say some of the undetermined deaths were probably suicides—if I could say it. But a coroner doesn’t have the legal option to say “probably”. There’s a long-held court ruling called the Beckon Test that states a death can only be classified as a suicide if it can be determined that the individual knew the consequences of their actions would end in death and intentionally carried them out. There is a high standard of proof required for a finding of suicide as the ruling states:
“In most legal cases the test to be satisfied is a balance of probability. But a determination of suicide can only be made where there is clear and convincing evidence. There is to be a presumption against suicide at the outset and one must be certain beyond a high degree of probability that the death was a suicide. Where one cannot be absolutely certain, the death must be classified as undetermined.”
Based on my death investigation experience, there are three points about Marilyn Monroe’s suicide ruling that bother me.
First, in all the polypharmacy overdoses I’ve seen where suicide was obvious, the deceased downed the whole darned stash. They wanted to end it all and get it done.
In Monroe’s case, Dr. Engelberg prescribed her 50 caps of 500 mg Chloral Hydrate on July 31 as a refill for a previous Chloral Hydrate order on July 25. She was taking 10 per day. At her death scene, there were still 10 Chloral Hydrate caps left in her bedside vial. 40 were gone and, at a rate of 10 per day from July 31 till August 4, the pill count is right in order.
In the toxicology world, the effects of drugs are rated on a range scale of Therapeutic, Toxic, and Lethal. In the Lethal range, the substance is given a value called LD50 where it’s expected that 50 percent of the population would be expected to die from the drug’s effect at a certain point based upon the drug’s milligram blood content per the kilogram weight of the person.
Marilyn Monroe’s autopsy report recorded her weight at 117 pounds or 53.2 kilograms. The Chloral Hydrate level in her blood was determined to be 8.0 milligrams (percent) based on her weight or 80 parts per million (ppm). Looking at my toxicology scale from my coroner days, I see that Chloral Hydrate has a Therapeutic range to 30 ppm and an LD50 value at 100 ppm, so Monroe was 20% under the Chloral Hydrate lethal bar.
Looking at her barbiturate blood content from the Nembutal, it’s recorded to be 4.5 mg (percent) or 45 ppm. My chart says the barbiturate Pentobarbital, which is what’s in Nembutal, has a Therapeutic range to 12 ppm and an LD50 at 40 ppm. So, Monroe was only 12.5 % over the average barbiturate lethal threshold, not taking into account that she was a very “tolerant” user.
However, the combination of Chloral Hydrate and Nembutal was deadly, and this had to be known by Dr. Engelberg when he ordered Monroe’s prescription. This brings me to my second point.
A physician has a professional duty of care to their patient, especially when prescribing medication to a person with Monroe’s mental history. I find it irresponsible, actually negligent, that Dr. Engelberg failed to ensure Monroe no longer had Chloral Hydrate in her possession when he issued her a prescription for 25, 1500 mg caps of Nembutal four days later, knowing her supply of Chloral Hydrate wasn’t exhausted based on her prescribed consumption.
My third point deals with the “rescue” issue.
This very much applies to the Beckon Test. Intentional overdoses as attention-getting devices are common and always rely on the person’s backup plan that someone will intervene. This was part of Monroe’s previous overdose episodes as noted in the “psychological autopsy” report. And they referenced Monroe’s locked door as being unusual.
I think the locked door issue is completely negated by the fact that Monroe was found with her telephone receiver in hand. This was stated by Eunice Murray, Dr. Greenson, Dr. Engelberg, and corroborated by the investigating detective who verified they reported this to him and suggested she was phoning for rescue—which was her pattern—but was overcome.
If I were the coroner ruling on Marilyn Monroe’s death classification, I’d be legally bound to consider how the facts apply to the category parameters.
A natural cause determination is completely eliminated by the autopsy and toxicology evidence. Monroe clearly died as the result of a drug overdose.
Despite kooky conspiracy theories that Bobby Kennedy snuck in and injected Marilyn Monroe to cover up her alleged affair with President Jack or that mobsters Jimmy Hoffa and Sam Giancana knocked her off to keep from ratting them out, no sensible person can make a case that Monroe was intentionally murdered. But a homicide ruling doesn’t just apply to murder. The definition of homicide is “the killing of a human being due to the act or omission of another”.
 I believe Dr. Engelberg was professionally negligent in his duty of care to Marilyn Monroe. He had to know—certainly ought to have known—that he was treating an emotionally unstable patient with a history of suicide attempts through polypharmacy. By giving Monroe a potentially lethal amount of barbiturates and not ensuring her chloral hydrate was gone, Engelberg effectively signed her death warrant.
I believe Dr. Engelberg was professionally negligent in his duty of care to Marilyn Monroe. He had to know—certainly ought to have known—that he was treating an emotionally unstable patient with a history of suicide attempts through polypharmacy. By giving Monroe a potentially lethal amount of barbiturates and not ensuring her chloral hydrate was gone, Engelberg effectively signed her death warrant.
However negligent Engelberg may have been, though, my suspicion falls short of the burden necessary for establishing a homicide classification.
That Monroe accidently died from a self-administered overdose is a distinct probability but, again, the Coroners Act and court precedents won’t allow me the liberty to rely on probabilities regarding suicide. I have to come to a clear conclusion based on facts.
Setting aside the locked door and phone receiver in hand—these two negate each other—I must defer to one other glaring fact. There were still 10 caps of Chloral Hydrate left in her pill vial. Marilyn Monroe was a very experienced and tolerant prescription pill user. She knew exactly what she was taking, what their effects were, and she failed to down her whole darned stash which is always proof of a polypharmacy overdose suicide.
 So, deferring to the Beckon Test, I have to presume against Marilyn Monroe’s suicide classification from the outset and must be satisfied beyond a high degree of probability that her death was a suicide—I must be certain—and I can’t—because no clear evidence exists that Monroe’s death was an intentional act to end her own life. It may well have been an unfortunate, un-rescued accident (which I suspect), but I can’t support that classification through the facts.
So, deferring to the Beckon Test, I have to presume against Marilyn Monroe’s suicide classification from the outset and must be satisfied beyond a high degree of probability that her death was a suicide—I must be certain—and I can’t—because no clear evidence exists that Monroe’s death was an intentional act to end her own life. It may well have been an unfortunate, un-rescued accident (which I suspect), but I can’t support that classification through the facts.
Therefore, I find Marilyn Monroe’s death classification as Undetermined.