Between The Bikers is the new release in my based-on-true-crime series. It’s Book #6 in a 12-part project that takes real cases and brings you, the reader, right inside actual criminal investigations with real cops and real crooks. I start each story with a warning about graphic content including gory scenes, sensitive techniques, and profane language. But that’s the real world of true crime. Here’s the online book description followed by the first two chapters of Between The Bikers.
Between The Bikers is the new release in my based-on-true-crime series. It’s Book #6 in a 12-part project that takes real cases and brings you, the reader, right inside actual criminal investigations with real cops and real crooks. I start each story with a warning about graphic content including gory scenes, sensitive techniques, and profane language. But that’s the real world of true crime. Here’s the online book description followed by the first two chapters of Between The Bikers.
Who had the most to gain by murdering a bad-ass biker—especially the powerful president of a Hells Angels Motorcycle Club chapter? The answer lies in Between The Bikers—Book 6 in the Based-On-True-Crime-Series by retired homicide detective and coroner, Garry Rodgers.
Mark Mitchell, aka Zeke, disappears on a Saturday afternoon just before a full-patch ceremony held between the bikers at a Hells Angels clubhouse on Vancouver Island in British Columbia at Canada’s west coast. The bikers are furious and the police are frantic to control an escalating mess that could lead to an all-out war within the Angels’ criminal organization. All fear a deadly underworld rift is about to explode.
While the bikers witch-hunt within their ranks and outside the law to ferret Zeke’s killers, the police urgently use every tactic and technique to solve the crime and contain the volatile gangsters. Wiretaps, surreptitious surveillance, clandestine operations, and highly-placed secret informants work through an unheard-of alliance between the bikers and their sworn enemies—the cops.
What happened to Zeke, and why, shocks both sides. The truth behind Mark Mitchell’s murder is something unmatched between the bikers who show the feared death head logo on their backs below the red-on-white words “Hells Angels”. It’s a truth known only by those with the most to gain—a truth that lies between the bikers.
——
 Between The Bikers comes with a warning: This book is based on a true crime story. Explicit descriptions of crime scenes, factual dialogue, real forensic procedures, highly-sensitive sources and actual police investigation, interview, and interrogation techniques are portrayed. Some names, times, and locations have been changed for privacy concerns and commercial purposes.
Between The Bikers comes with a warning: This book is based on a true crime story. Explicit descriptions of crime scenes, factual dialogue, real forensic procedures, highly-sensitive sources and actual police investigation, interview, and interrogation techniques are portrayed. Some names, times, and locations have been changed for privacy concerns and commercial purposes.
This is the sixth story in the Based-On-True-Crime Series by Garry Rodgers. Other titles include In The Attic, Under The Ground, From The Shadows, Beside The Road, and On The Floor. Reviewers describe Rodgers’ story-telling style as a 21st century Joseph Wambaugh using Elmore Leonard dialogue with plot, pacing, and characterization in the flare of Fiona Barton and Paula Hawkins.
* * *
BETWEEN THE BIKERS
Chapter One — Monday, April 27th – 8:20 a.m.
“Zeke’s missing.” Harry clomped into our Serious Crimes Section. She plopped herself down in her desk chair. “Word is he’s been done in.”
“Well, if he’s been whacked…” I rolled back from my cubicle and smiled at my detective partner, Harry. “It’ll be between the bikers.”
“Yup.” Harry took a slurp from her stainless Starbucks mug. “I took a spin by the Hells Angels clubhouse. They’re swarming like ants on a fucking hill.”
“Your word… how good is it?” Harry had my full attention.
“Like, my word?” She smiled back. “Impeccable. Obviously, you know that.”
“No, shithead. Not your word. I meant, who’d you hear this from?”
Harry took another pull from her cup. She subconsciously looked from side to side. “Don Ransom at Drug Squad. His wiretaps and cameras are lit up like Times Square.”
“Okay.” I nodded and leaned in. “Something’s going on. Someone’s stuck a honey-coated stick in the ant pile.”
“I stopped by Drugs this morning about something else.” Harry lowered her voice. “The guys are working flat-out, interpreting audio intercepts and video surveillance. Looks like the HAs are preparing for all-out war with whoever hit Zeke. Don’s pretty sure Zeke’s dead and you know what that means.”
“Yeah.” I moved back. “We’re going to inherit Zeke’s fuckin’ mess.”
 By “we”, I meant the detectives at Nanaimo Serious Crimes Section. And by “Zeke”, I meant Mark Mitchell, who was the president of the Nanaimo Hells Angels Motorcycle Club chapter. Zeke was Mark Mitchell’s nickname, and he was well known—very well known—to our police department.
By “we”, I meant the detectives at Nanaimo Serious Crimes Section. And by “Zeke”, I meant Mark Mitchell, who was the president of the Nanaimo Hells Angels Motorcycle Club chapter. Zeke was Mark Mitchell’s nickname, and he was well known—very well known—to our police department.
Nanaimo is a small seaside city of a hundred thousand, set on the southeast side of Vancouver Island. It’s right across from the City of Vancouver in British Columbia, Canada which is one of the most exotic, erotic, and expensive places in the world.
Although Nanaimo is cut off by water from the B.C. mainland, it takes on the same crime characteristics as a large metropolis. Nanaimo has its share of serious stuff like murders, rapes, robberies, extortions, arsons, loansharking, and money laundering. There are homeless and junkies begging on the street, and well-paid prostitutes doing their thing with high-profile clients behind closed doors.
 Nanaimo has graft in the civic circles and grief at the street scene. Most grief is caused by addicts and mental cases that have no hope for treatment, never mind a chance at recovery. There are losers on welfare and gambling fanatics, thieves and tag-artists, as well as pot-growers and meth-cookers. And there’s a subculture that profits from bottom-feeders and contributes to nothing but trouble and tragedy—the bikers.
Nanaimo has graft in the civic circles and grief at the street scene. Most grief is caused by addicts and mental cases that have no hope for treatment, never mind a chance at recovery. There are losers on welfare and gambling fanatics, thieves and tag-artists, as well as pot-growers and meth-cookers. And there’s a subculture that profits from bottom-feeders and contributes to nothing but trouble and tragedy—the bikers.
The Nanaimo Hells Angels chapter, or charter as the outlaw motorcycle club is sometimes called, had a regular complement of about thirteen guys. That was give or take a few that may have quit, got fired, been jailed, or suddenly disappeared, like what had happened to Zeke. And what happened to Zeke was unlike anything anyone in our Serious Crimes Section ever experienced.
Serious Crimes in Nanaimo was part of the police department’s support services that assisted the rank-and-file General Duty or Patrol division. Harry and I were a team of two assigned to investigate complicated and time-consuming files that patrol officers couldn’t stick with. There were other two-person teams as well as an overall detective boss, Staff Sergeant Leaky Lewis.  Leaky also supervised Drug Squad, Forensics, Property Crimes, Street Crew, Sex Crimes, Commercial Crimes, and one poor prick plagued with mitigating frauds and bad plastic.
Leaky also supervised Drug Squad, Forensics, Property Crimes, Street Crew, Sex Crimes, Commercial Crimes, and one poor prick plagued with mitigating frauds and bad plastic.
Harry, by the way, was not my partner’s real name. She was Sheryl Henderson, a large lady with large hair and an even larger personality. We called Sheryl “Harry” after the bigfoot or sasquatch in the movie Harry and The Hendersons.
“So what else did you find out at Drug Squad?” I’d stopped smiling. It quickly sunk in that, although Zeke’s loss would be the community’s gain, there would be hell to pay in fallout. Intrinsically, I knew—or thought I knew—that whatever happened to Mark Mitchell, aka Zeke, would be an issue between the bikers, and I knew that the biker mentality would not take this lying down.
Harry took another sip from her Starbucks cup, which was as tarnished and dented as a few parts of her career. “So, what Don Ransom tells me is that Zeke was last seen on Saturday afternoon. He’d been over to Vancouver to pick up some rings for a patch-over ceremony that was supposed to happen on Saturday night. He fell off the radar and hasn’t flown since.”
“Rings?”
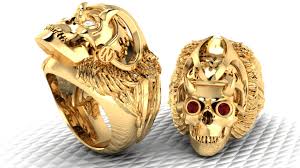 “Yeah.” Harry examined her cup and picked at something caked on it. “Biker rings. You know those gold death head things that full-patches wear?”
“Yeah.” Harry examined her cup and picked at something caked on it. “Biker rings. You know those gold death head things that full-patches wear?”
“Oh, yeah. Biker rings.”
“They’re clunky and gaudy if you want my opinion.” Harry kept picking. “Anyway, they’re an initiation gift for someone who is accepted full-time into the club. So Zeke got the rings but hasn’t been heard from since.”
“Hey. Wait a minute.” I smiled again. “You mean he was last seen in Vancouver? He disappeared in Vancouver? Then it’s not our problem.”
Harry did the time-out sign. “No. Not so lucky there, Louie. Zeke made it back from Vancouver. His truck was found abandoned here. Beside the Harewood Arms pub. Locked. Keys gone. Zeke gone.”
“Fuuuck—”
Harry waved her finger. “You know the last-seen rule. He was last seen here in Nanaimo so that does make it our fucking problem. Wish it weren’t so, but it is so. We’re stuck with finding out what’s happened to Zeke.”
I wished it weren’t so, too. The last thing I needed as an old cop ready to retire was refereeing a ferocious fight between the bikers.
Chapter Two — Monday, April 27th – 8:50 a.m.
 Leaky Lewis called Harry and me into his office. He closed the door and nudged us towards two wooden chairs in front of his solid oak desk. His blinds were shut tight, but his lights were on bright, giving the room sort of an unnerving feel.
Leaky Lewis called Harry and me into his office. He closed the door and nudged us towards two wooden chairs in front of his solid oak desk. His blinds were shut tight, but his lights were on bright, giving the room sort of an unnerving feel.
That was far from the case when dealing with Leaky. As a boss, it was hard to find anyone fairer and, as a person, you couldn’t find anyone more approachable. I’d known Leaky since he was a new-hire in the Nanaimo police department. He’d quickly climbed the ladder and was now officially ranked as a Detective Staff Sergeant, making him my direct supervisor.
Almost all cops get nicknames. They’re usually earned from a play-on-words, or some career-haunting mishap. Leaky was Jim Lewis. He got the moniker because he suffered a chronic case of post-urinary drip.
“So something’s happened to Zeke, I hear.” Leaky looked at Harry and me with a neutral expression. “Where are we going to go with this?”
Harry and I hesitated to answer.
“This isn’t a trick question.” Leaky grinned. “Seriously. I want some input on how we’re going to handle this, ah, situation.”
 “I’d like to say we do fuck-all.” I grinned back. “But… we all know that if someone’s offed Zeke, then someone’s going to pay for it and someone else is going to pay for that and we’re going to be into a full-on biker war. And I don’t want no part of that at this stage of my game.”
“I’d like to say we do fuck-all.” I grinned back. “But… we all know that if someone’s offed Zeke, then someone’s going to pay for it and someone else is going to pay for that and we’re going to be into a full-on biker war. And I don’t want no part of that at this stage of my game.”
Leaky nodded and looked at Harry. “Your take?”
One thing about Harry, she wasn’t afraid to speak her mind.
“We got to get on this right away. I have no doubt he’s right.” Harry thumbed at me. “This could be a fucking blood bath if we don’t go right out and get in their faces.”
“Don Ransom told me he’s never heard the Angels talk so openly on their phones.” Leaky shuffled in his chair. “Don’s had them wired up for a long time… off and on… and he knows their pattern. He says they sound rattled. Confused. Trying to make sense of what’s going on. Don thinks the Nanaimo chapter really doesn’t know what’s happened. They’re scrambling for clues.”
Harry continued. “From what Don told me an hour ago, and what I saw when I drove past the clubhouse, I think the HA full-patches are going to start grabbing people here, there, and all over and muscle them for information. This thing will escalate real fast unless we show a lot of force, and right away. They have to know we’re not going to let them run the fucking show around here.”
Leaky nodded again. “Show of force? How do you see doing that?”
 Harry already had a plan in her mind. “A big drive-by back and forth at the clubhouse. Setting up the command center mobile at the edge of their property. Leaving the cameras on twenty-four seven. Even hovering Air One on top of their fucking room. Let them know we’re not going to let a biker war start or we’ll bug-squash them.”
Harry already had a plan in her mind. “A big drive-by back and forth at the clubhouse. Setting up the command center mobile at the edge of their property. Leaving the cameras on twenty-four seven. Even hovering Air One on top of their fucking room. Let them know we’re not going to let a biker war start or we’ll bug-squash them.”
Leaky didn’t nod. “I’m not so sure… It might just agitate them even more. I think we should watch all right. But, I think we should rely on intel with sources already in place. Some intel is just starting to come in. Don called me just before you guys sat down and says he’s going to come here and talk in person. Let’s wait for what he has. What about the basics… like opening a file and deciding who’s going to coordinate this. After all, we don’t even have an official complaint.”
Harry shrugged. “The paperwork can wait. I say we get right out there and fly the flag before they decide to run away with biker law.”
Leaky stood up. It wasn’t like he was mad or upset, but more like he was starting to feel uncomfortable. “I’m also thinking of opening a communication channel. Like going right to the leader and simply asking him what’s going on.”
 “Their leader is missing.” Harry made a good point. “Zeke is, was, whatever, the president. He has, or had, been for a long time.”
“Their leader is missing.” Harry made a good point. “Zeke is, was, whatever, the president. He has, or had, been for a long time.”
Leaky nodded again. “Fred Wallacott is the past-president. He’s been with the club since they were the 101 Knights and the Satan’s Angels. I’ve known Fred since college. Not that we were ever friends or buddies or anything. But I think I can talk to him.”
I spoke up. “I have a reasonable rapport with Fred Wallacott. Big Wally as they call him. It might be best if I talk to him in private… away from the club scene.”
Harry gave me a quizzical eye. “I didn’t know that. What’s your connection to Fred Wallacott?”
“I don’t go around advertising it, but we’ve gotten to know each other semi-socially over the years.”
Harry laughed. “You? Partying with the fucking Hells Angels?”
“No. Not partying. Our kids traveled in the same circles. Fred’s daughter and my daughter went to Highland dance classes and gymnastic classes together. Fred’s son and my son went to kickboxing lessons together. So I’d regularly run into Fred—two dads dropping off and picking up kids—and then I’d see him at events like graduations, competitions, and demonstrations.”
Harry stopped laughing. “You think you can actually talk to a fucking biker like one-on-one?”
“I know I can.”
“You’re serious about this?”
 “Yeah. I know he’s big and intimidating and has this tough-guy biker persona. Deep down, Fred’s a reasonable guy. Actually—very well-read and informed. Tell you a funny story about Fred. He has a bunch of rental properties around town. Once, he had to serve an eviction notice and didn’t want to get into a violent situation where the guy could press charges against him. So, Fred came into the police station and asked for a plainclothes officer to stand by to keep the peace while he hangs paper on the tenant. We go over to Fred’s block. He knocks on the door. Guy opens it and refuses to take the notice so Fred takes out his Buck knife and jams it into the door, face-pinning the paper, and says, ‘Here. You’re fucking served’. Then we just left.”
“Yeah. I know he’s big and intimidating and has this tough-guy biker persona. Deep down, Fred’s a reasonable guy. Actually—very well-read and informed. Tell you a funny story about Fred. He has a bunch of rental properties around town. Once, he had to serve an eviction notice and didn’t want to get into a violent situation where the guy could press charges against him. So, Fred came into the police station and asked for a plainclothes officer to stand by to keep the peace while he hangs paper on the tenant. We go over to Fred’s block. He knocks on the door. Guy opens it and refuses to take the notice so Fred takes out his Buck knife and jams it into the door, face-pinning the paper, and says, ‘Here. You’re fucking served’. Then we just left.”
Leaky and Harry laughed.
Leaky brought us back to the business at hand. “I know you’re rammy, Harry, and you want to show them our colors. And, you might be right about that. We can use that as plan B, but first I want to get as much info on this as possible. Looking at this objectively, we don’t even know if Zeke is dead. He might be abducted and held for some biker reason. For that matter, he might have even fucked off and faked his own disappearance.”
I agreed with Leaky. “Let’s take this a step at a time. Like, we don’t even have an official missing person complaint to start sticking our noses into. Let’s get our source intel and then do a back-channel move. After that, we can show all the muscle we want.”
There was a rap at the door. It opened. In came Don Ransom with breaking biker news.
Get the Between The Bikers eBook at: