 There’s something ingrained in humans that cause us to take dangerous risks and try things that might change the world. Over the course of civilization, thousands upon thousands of inventions succeeded beyond their creator’s wildest dream. But some were epic fails. Here’s a look at the top 20 inventors who were killed by their own inventions.
There’s something ingrained in humans that cause us to take dangerous risks and try things that might change the world. Over the course of civilization, thousands upon thousands of inventions succeeded beyond their creator’s wildest dream. But some were epic fails. Here’s a look at the top 20 inventors who were killed by their own inventions.
20. Thomas Andrews was the chief naval architect for the R.M.S. Titanic and it was his honor to accompany the ship on its maiden voyage. Andrews was aware of the Titanic’s vulnerability in ice-laden waters and originally called for the Titanic to be double-hulled and equipped with forty-six lifeboats, instead of the twenty it actually carried. He was overruled due to cost constraints. When the Titanic struck the iceberg on April 15, 1912, Andrews heroically helped many people into the lifeboats. He was last seen in the first-class smoking lounge, weeping. His body was never recovered.
19. William Bullock invented the first modern printing press. While installing a machine for the Philadelphia Public Ledger, Bullock tried to kick a belt onto a pulley and got his leg crushed in the moving mechanism. He quickly developed gangrene and his leg needed amputating. During his surgery on April 12, 1867, Bullock died of complications.
 18. Francis Edgar Stanley invented the photographic dry plate which he sold to George Eastman of Eastman-Kodak fame. With the profits, he founded the Stanley Motor Carriage Company and developed a line of steam-powered automobiles called Stanley Steemers. On July 13, 1918, Francis Stanley was testing one of his Steemers and swerved to miss some farm animals. He plowed into a wood pile and died.
18. Francis Edgar Stanley invented the photographic dry plate which he sold to George Eastman of Eastman-Kodak fame. With the profits, he founded the Stanley Motor Carriage Company and developed a line of steam-powered automobiles called Stanley Steemers. On July 13, 1918, Francis Stanley was testing one of his Steemers and swerved to miss some farm animals. He plowed into a wood pile and died.
17. Jean-Francoise Pilatre de Rozier was a French chemistry and physics teacher as well as being the true father of aviation. He made the first hot air balloon flight in 1783. He was also the first to experiment with hydrogen as a propellant, testing it by taking a mouthful and blowing it across an open flame. After losing his hair and eyebrows, he dismissed hydrogen as being too volatile—something the makers of the Hindenburg would later confirm. On July 15, 1785, de Rozier attempted to cross the English Channel in his balloon. It crashed, killing de Rozier and his passenger.
16. Louis Slotin was an American nuclear physicist who worked on the Manhatten Project. After the war, Slotin continued to experiment with plutonium and accidently set off a fission reaction which released a hard burst of radiation. Realizing what he’d done, Slotin heroically covered the material with his body while the others made a run for the hills. He died on May 30, 1946, two weeks after the exposure.
 15. Karel Soucek was a Czechoslovakian daredevil and inventor. He built a specially-designed, shock-proof barrel and repeatedly flowed over Niagara Falls. To top this feat, Soucek invented a new capsule which was dropped from the roof of the Houston Astrodome on January 20, 1985. It missed its target, which was a small water container, and Soucek was killed on impact. World-renown stuntman, Evel Knievel, tried to talk Soucek out of it, saying “It was the most dangerous thing I’ve ever seen.”
15. Karel Soucek was a Czechoslovakian daredevil and inventor. He built a specially-designed, shock-proof barrel and repeatedly flowed over Niagara Falls. To top this feat, Soucek invented a new capsule which was dropped from the roof of the Houston Astrodome on January 20, 1985. It missed its target, which was a small water container, and Soucek was killed on impact. World-renown stuntman, Evel Knievel, tried to talk Soucek out of it, saying “It was the most dangerous thing I’ve ever seen.”
14. Sylvester H. Roper invented the world’s first motorcycle. He called it a velocipede and it was actually a converted bicycle powered by a steam engine. On June 01, 1896, Roper was testing the machine on a bicycle racing track and was lapping the pedal-powered two-wheelers at over forty mph. Suddenly, he wiped out and died. The autopsy showed the cause of death to be a heart attack, but it’s not known if the attack caused the crash or if the crash caused the attack. He was seventy-two.
13, Horace Lawson Hunley invented the submarine. His first prototype trapped seven sailors underwater and killed them all. Hunley went back to the drawing board and came up with a new and improved sub, aptly named the H.L. Hunley, which he skippered himself. On October 15, 1863, Hunley was testing the Hunley off the coast of Charleston, South Carolina, when it failed to surface and again killed the crew—including Hunley himself.
 12. Aurel Viaicu was a Romanian inventor and test pilot of his own line of aircraft, called the Vlaicu WR I, II, and III. He achieved many notable firsts such as the highest, longest, and fastest flights. On Friday, September 13, 1913, Vlaicu’s luck ran out when he attempted the highest altitude flight ever—crossing the peaks of the Carpathian Mountains. The cause of the crash was never determined.
12. Aurel Viaicu was a Romanian inventor and test pilot of his own line of aircraft, called the Vlaicu WR I, II, and III. He achieved many notable firsts such as the highest, longest, and fastest flights. On Friday, September 13, 1913, Vlaicu’s luck ran out when he attempted the highest altitude flight ever—crossing the peaks of the Carpathian Mountains. The cause of the crash was never determined.
11. Valerian Abakovsky invented the Aerocar, also known as the Aerowagon, which was a steam-powered, propeller-driven rail car intended to whisk railway executives quickly across the vast lands of Siberia. On July 24, 1921, the twenty-five-year-old Abakovsky was whirling a group of twenty-two big-shots from Tula to Moscow when he approached a curve at over one hundred mph. His Aerocar went airborne and killed six, including the inventor.
10. Marie Curie was a Polish chemist/physicist who pioneered research into radioactivity and won the Nobel Prize—twice. Besides proposing the theory of radiation and discovering two elements, she is credited with inventing radiography or X-rays. Curie died on July 14, 1934, in a French sanatorium from aplastic anemia due to long-term exposure to radiation, probably from her habit of carrying test-tubes of plutonium in her pockets.
 9. James Fuller “Jim” Fixx didn’t exactly invent running but he popularized it through his mega-bestselling book Complete Book Of Running. Fixx took up the sport after a lifetime of stress and bad habits. He became a world celebrity on fitness and healthy living. On the morning of July 20, 1984, he was out for his daily running fix and fell dead in his tracks on Route 15 in Hardwick, Vermont. His official cause of death was a fulminant heart attack. The autopsy showed his heart arteries were 70% blocked in the right anterior descending, 80% blocked in the left anterior descending, and 95% blocked in the circumflex. Runner Jim Fixx was fifty-two.
9. James Fuller “Jim” Fixx didn’t exactly invent running but he popularized it through his mega-bestselling book Complete Book Of Running. Fixx took up the sport after a lifetime of stress and bad habits. He became a world celebrity on fitness and healthy living. On the morning of July 20, 1984, he was out for his daily running fix and fell dead in his tracks on Route 15 in Hardwick, Vermont. His official cause of death was a fulminant heart attack. The autopsy showed his heart arteries were 70% blocked in the right anterior descending, 80% blocked in the left anterior descending, and 95% blocked in the circumflex. Runner Jim Fixx was fifty-two.
8. Max Valier was an Austrian rocket scientist who invented solid and liquid fueled missiles. Given his success with flight, Valier thought it’d be cool to make a rocket-propelled car. It worked, too, and he got it up to 250 mph. Trying to get even better, Valier experimented with alcohol as a combustible. That got away on him and blew up on his workbench, killing Valier and burning his workshop down.
7. Alexander Bogdanov was a Russian physician, writer, politician, and inventor of sorts. He was a major player in the 1917 Bolshevik Revolution and ended up in jail. He talked his way out of death row and back into medicine where he became obsessed with blood. Bogdanov founded the Institute For Haematology and was convinced that blood transfusion was the ticket to the fountain of youth. To back up his beliefs, he used himself as a crash-test dummy and transfused blood from a patient suffering malaria and tuberculosis into his own system. He died two days later on April 07, 1928, but the patient slowly got better. It seems that the blood types were incompatible—something little known in the day.
 6. Otto Lilienthal was known as The Glider King. A German pioneer in aviation, Lilienthal made over 2,000 glider flights and is credited with perfecting the gull-wing design and set the long-held record of soaring to 1820 feet. On August 10, 1896, Lilienthal experimented with “shifting weight” in a glider at fifty feet. It lost lift, stalled, and he augered into the ground, breaking his neck.
6. Otto Lilienthal was known as The Glider King. A German pioneer in aviation, Lilienthal made over 2,000 glider flights and is credited with perfecting the gull-wing design and set the long-held record of soaring to 1820 feet. On August 10, 1896, Lilienthal experimented with “shifting weight” in a glider at fifty feet. It lost lift, stalled, and he augered into the ground, breaking his neck.
5. Li Si died in 208 BC at age seventy-two of The Five Pains. That was a form of torture or “punishments” involving tattooing the face, cutting off the nose, cutting off the feet, castration, and finally death by exposure. Li Si was Prime Minister during China’s Qin Dynasty and fell out of favor with the Emperor. It should be noted Li Si invented The Five Pains.
4. Henry Smolinski held a degree in aeronautical engineering from the Northrup Institute Of Technology. Old Hank got it in his head that a flying car would be a good idea so he bastardized the boxed-wing rear section of a Cessna 337 Skymaster and welded it onto the top of a ’71 Ford Pinto. He actually got the thing to fly. On September 11, 1973, Hank took his buddy, Harold Blake, up for a spin in the Pinto-cross. At around three hundred feet, one of the wings snapped and the pony-car-plane bucked them off to a fiery death. The Transportation Safety Board investigated and said there was nothing wrong with Hank’s design, just that his welding was the shits.
3. Abu Nasr Ismail ibn Hammad a-Jawhari died around 1008 AD at Nishapur which is in today’s Iraq. He was a Muslim cleric, scholar, and a bit of an inventor. He was fascinated with flight so he built a pair of feather-covered, wooden wings and strapped them to his back and arms. To impress the Iman, Mr. a-Jawhari jumped off the roof of the mosque hoping they’d work. They didn’t, but to commemorate the first known attempt at human flight, they built a mural on the wall of the mosque. It’s actually quite pretty.
2. Wan-Hoo may, or may not, have been real. Some say he was apocryphal, or doubtful, but one thing’s for sure—he’s a legend. Wan-Hoo was reported to be a 16th-century Chinese official who tried to shoot himself to the moon by attaching forty-seven rockets to a chair and lighting them all at once. They say there was this huge bang and, when the smoke cleared, Wan-Hoo and his chair were nowhere to be found. Today, there’s a crater on the moon named after Wan-Hoo, and I’m not making this up.
 1. Franz Reichelt was real—a real stupid sonofabitch if there ever was one. He was known as The Flying Tailor and is credited with inventing the coat parachute. To prove it worked, he conned the keepers of the Eifel Tower to let him demonstrate. On February 04, 1912, Franz held a major press venue so they could witness his inaugural jump. He leaped from the first deck and gravity took over. It was captured on film and today you can watch this moron splat himself on YouTube.
1. Franz Reichelt was real—a real stupid sonofabitch if there ever was one. He was known as The Flying Tailor and is credited with inventing the coat parachute. To prove it worked, he conned the keepers of the Eifel Tower to let him demonstrate. On February 04, 1912, Franz held a major press venue so they could witness his inaugural jump. He leaped from the first deck and gravity took over. It was captured on film and today you can watch this moron splat himself on YouTube.











 A massive molasses storage tank ruptured in downtown Boston, Massachusetts at 12:40 pm on Wednesday, January 15, 1919. 2.3 million gallons of liquid sludge, weighing over 12,000 tons, burst from the receptacle and sent a surge of brown death onto Boston’s streets. The sickly sweet wave was 40 feet high and moved at 35 miles per hour. When the sugary flood stopped, 21 people were dead and over 150 suffered injuries. Property damage was in the millions, and the legal outcome changed business practices across America. Sadly, the Boston Molasses Disaster, or Boston Molasses Flood, was perfectly preventable.
A massive molasses storage tank ruptured in downtown Boston, Massachusetts at 12:40 pm on Wednesday, January 15, 1919. 2.3 million gallons of liquid sludge, weighing over 12,000 tons, burst from the receptacle and sent a surge of brown death onto Boston’s streets. The sickly sweet wave was 40 feet high and moved at 35 miles per hour. When the sugary flood stopped, 21 people were dead and over 150 suffered injuries. Property damage was in the millions, and the legal outcome changed business practices across America. Sadly, the Boston Molasses Disaster, or Boston Molasses Flood, was perfectly preventable.
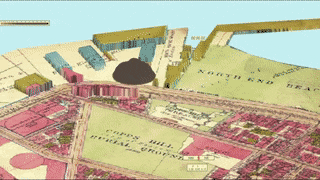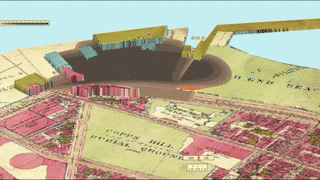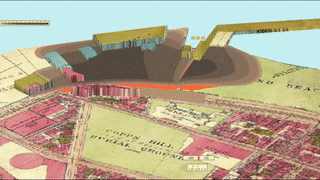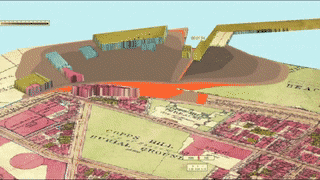
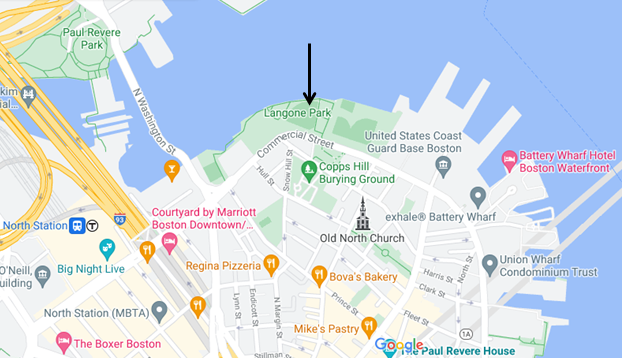
 If the tank wasn’t ready, the USIA executives would have to find another storage facility (of which there were none that size in America) or dump the molasses at sea. Either way was a major loss for USIA and for Arthur Jell himself.
If the tank wasn’t ready, the USIA executives would have to find another storage facility (of which there were none that size in America) or dump the molasses at sea. Either way was a major loss for USIA and for Arthur Jell himself.
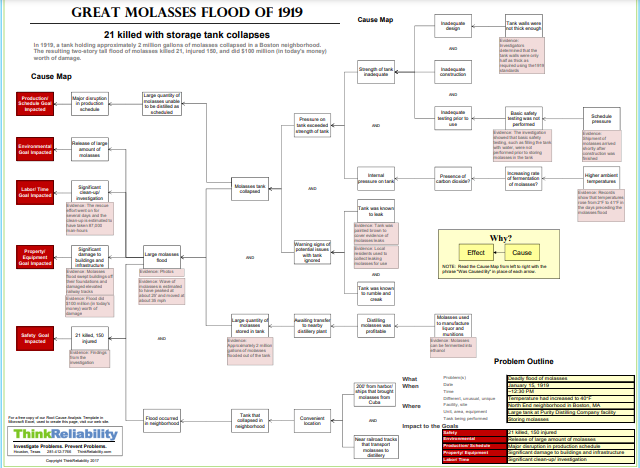
 The presiding judge didn’t buy the explosion argument. In his judgment finding complete fault on behalf of Purity and USIA, the judge wrote, “The tank was wholly insufficient in point of structural strength, insufficient to meet either legal or engineering requirements. The scene was unparalleled in the severity of the damage inflicted to the person and property from the escape of liquid from any container in a great city.” In conclusion, the judge ordered USIA to pay the plaintiffs $628,000 which is approximately $10.12 million in today’s currency.
The presiding judge didn’t buy the explosion argument. In his judgment finding complete fault on behalf of Purity and USIA, the judge wrote, “The tank was wholly insufficient in point of structural strength, insufficient to meet either legal or engineering requirements. The scene was unparalleled in the severity of the damage inflicted to the person and property from the escape of liquid from any container in a great city.” In conclusion, the judge ordered USIA to pay the plaintiffs $628,000 which is approximately $10.12 million in today’s currency.