This material is based on an article by Dr. C. Truman Davis and first published by the Christian Broadcasting Network. This appears to be a very factual look at how Jesus Christ really died.
 Some time ago after reading Jim Bishop’s The Day Christ Died, I realized that for years I’d taken the Crucifixion more or less for granted — I’d grown callous to its horror by a too easy familiarity with the grim details and a too distant relationship with Jesus. Now, at Easter, it occurred to me that even with a significant background in medical death investigation, I didn’t know anything about the actual anatomical cause of Jesus Christ’s death.
Some time ago after reading Jim Bishop’s The Day Christ Died, I realized that for years I’d taken the Crucifixion more or less for granted — I’d grown callous to its horror by a too easy familiarity with the grim details and a too distant relationship with Jesus. Now, at Easter, it occurred to me that even with a significant background in medical death investigation, I didn’t know anything about the actual anatomical cause of Jesus Christ’s death.
The Gospel writers don’t help us much on this point because crucifixion and scourging were so common during their lifetime that they apparently considered a detailed description unnecessary. So we have only the concise words of the Evangelists: “Pilate, having scourged Jesus, delivered Him to them to be crucified — and they crucified Him.”
I have no competence to discuss the infinite psychic and spiritual suffering of the Incarnate God atoning for the sins of fallen man. I honestly don’t understand that. But I was curious about investigating the physiological and anatomical aspects of the Lord’s passion in detail.
 What did the body of Jesus of Nazareth actually endure during those hours of torture?
What did the body of Jesus of Nazareth actually endure during those hours of torture?
This led first to a study of the practice of crucifixion itself; that is, torture and execution by fixation to a cross. I’m indebted to many who’ve studied this subject in the past — especially Dr. Pierre Barbet, a French surgeon who’s done exhaustive historical and experimental research and written extensively on the subject.
Apparently, the first known practice of crucifixion was by the Persians. Alexander and his generals brought it back to the Mediterranean world — to Egypt and to Carthage. The Romans learned the practice from the Carthaginians and (as with almost everything the Romans did) rapidly developed a very high degree of efficiency and skill at it. A number of Roman authors (Livy, Cicer, Tacitus) comment on crucifixion. Several innovations, modifications, and variations are described in the ancient literature.
 For instance, the upright portion of the cross (or stipes) could have the cross-arm (or patibulum) attached two or three feet below its top in what we commonly think of as the Latin cross. The most common form used in Jesus’s day, however, was the Tau cross, shaped like our T.
For instance, the upright portion of the cross (or stipes) could have the cross-arm (or patibulum) attached two or three feet below its top in what we commonly think of as the Latin cross. The most common form used in Jesus’s day, however, was the Tau cross, shaped like our T.
In this cross, the patibulum was placed in a notch at the top of the stipes. There is archeological evidence that it was on this type of cross that Jesus was crucified. Without any historical or biblical proof, Medieval and Renaissance painters have given us our picture of Christ carrying the entire cross. But the upright post, or stipes, was generally fixed permanently in the ground at the site of execution and the condemned man was forced to carry the patibulum, weighing about 110 pounds, from the prison to the place of execution.
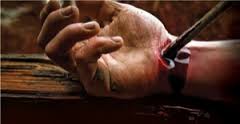 Many of the painters and most of the sculptors of crucifixion also show the nails through the palms. Historical Roman accounts and experimental work have established that the nails were driven between the small bones of the wrists (radial and ulna) and not through the palms. Nails driven through the palms will strip out between the fingers when made to support the weight of the human body. The misconception may have come about through a misunderstanding of Jesus’ words to Thomas, “Observe my hands.” Anatomists, both modern and ancient, have always considered the wrist as part of the hand.
Many of the painters and most of the sculptors of crucifixion also show the nails through the palms. Historical Roman accounts and experimental work have established that the nails were driven between the small bones of the wrists (radial and ulna) and not through the palms. Nails driven through the palms will strip out between the fingers when made to support the weight of the human body. The misconception may have come about through a misunderstanding of Jesus’ words to Thomas, “Observe my hands.” Anatomists, both modern and ancient, have always considered the wrist as part of the hand.
A titulus, or small sign, stating the victim’s crime was usually placed on a staff, carried at the front of the procession from the prison and later nailed to the cross so that it extended above the head. This sign with its staff nailed to the top of the cross would have given it somewhat the characteristic form of the Latin cross.
 But the physical passion of Christ began in Gethsemane. Of the many aspects of this initial suffering, the one of greatest physiological interest is the bloody sweat. It is interesting that St. Luke, the physician, is the only one to mention this. He says, “And being in agony, He prayed the longer. And His sweat became as drops of blood, trickling down upon the ground.” Every ruse (trick) imaginable has been used by modern scholars to explain away this description, apparently under the mistaken impression that this just doesn’t happen. A great deal of effort could have been saved had the doubters consulted medical literature.
But the physical passion of Christ began in Gethsemane. Of the many aspects of this initial suffering, the one of greatest physiological interest is the bloody sweat. It is interesting that St. Luke, the physician, is the only one to mention this. He says, “And being in agony, He prayed the longer. And His sweat became as drops of blood, trickling down upon the ground.” Every ruse (trick) imaginable has been used by modern scholars to explain away this description, apparently under the mistaken impression that this just doesn’t happen. A great deal of effort could have been saved had the doubters consulted medical literature.
Though very rare, the phenomenon of Hematidrosis, or bloody sweat, is well documented. Under great emotional stress of the kind Jesus suffered, tiny capillaries in the sweat glands can break, thus mixing blood with sweat. This process might well have produced marked weakness and possible shock.
 After the arrest in the middle of the night, Jesus was brought before the Sanhedrin and Caiphus, the High Priest. It’s here the first physical trauma was inflicted. A soldier struck Jesus across the face for remaining silent when questioned by Caiphus. The palace guards then blindfolded him and mockingly taunted him to identify them. As each passed by, they spat upon Jesus and struck him in the face.
After the arrest in the middle of the night, Jesus was brought before the Sanhedrin and Caiphus, the High Priest. It’s here the first physical trauma was inflicted. A soldier struck Jesus across the face for remaining silent when questioned by Caiphus. The palace guards then blindfolded him and mockingly taunted him to identify them. As each passed by, they spat upon Jesus and struck him in the face.
In the early morning — battered, bruised, dehydrated and exhausted from a sleepless night — Jesus was taken across the Praetorium of the Fortress Antonia, the seat of government of the Procurator of Judea, Pontius Pilate. Pilate passed responsibility to Herod Antipas, the Tetrarch of Judea. Jesus apparently suffered no physical mistreatment at the hands of Herod and was returned to Pilate.
It was then, in response to the cries of the mob, that Pilate ordered Bar-Abbas released and condemned Jesus to scourging and crucifixion.
 There is much disagreement among authorities about the unusual scourging as a prelude to crucifixion. Most Roman writers from this period do not associate the two. Many scholars believe that Pilate originally ordered Jesus scourged as his full punishment and that the death sentence by crucifixion came only in response to the taunt by the mob that the Procurator was not properly defending Caesar against this pretender who allegedly claimed to be the King of the Jews.
There is much disagreement among authorities about the unusual scourging as a prelude to crucifixion. Most Roman writers from this period do not associate the two. Many scholars believe that Pilate originally ordered Jesus scourged as his full punishment and that the death sentence by crucifixion came only in response to the taunt by the mob that the Procurator was not properly defending Caesar against this pretender who allegedly claimed to be the King of the Jews.
Preparations for the scourging were carried out when Jesus was stripped of his clothing and his hands tied to a post above his head. It’s doubtful the Romans would have made any attempt to follow the Jewish law in this matter but the Jews had an ancient law prohibiting more than forty lashes. The Roman legionnaire stepped forward with the flagrum (or flagellum) in his hand. This is a short whip consisting of several heavy, leather thongs with two small balls of lead attached near the ends of each. The heavy whip was brought down with full force again and again across Jesus’ shoulders, back, and legs.
 At first, the thongs cut through the skin only. Then, as the blows continued, they cut deeper into the subcutaneous tissues producing first an oozing of blood from the capillaries and veins of the skin then finally spurting arterial bleeding from vessels in the underlying muscles. The small balls of lead produced large, deep bruises which were broken open by subsequent blows. Finally, the skin of Jesus’s back would be hanging in long ribbons and the entire area an unrecognizable mass of torn, bleeding tissue.
At first, the thongs cut through the skin only. Then, as the blows continued, they cut deeper into the subcutaneous tissues producing first an oozing of blood from the capillaries and veins of the skin then finally spurting arterial bleeding from vessels in the underlying muscles. The small balls of lead produced large, deep bruises which were broken open by subsequent blows. Finally, the skin of Jesus’s back would be hanging in long ribbons and the entire area an unrecognizable mass of torn, bleeding tissue.
When it was determined by the centurion in charge that Jesus was near death, the beating finally stopped. The half-fainting Jesus was untied and allowed to slump to the stone pavement, wet with his own blood.
 The Roman soldiers saw a great joke in this provincial Jew claiming to be king. They threw a robe across his shoulders and placed a stick in his hand for a scepter. They still needed a crown to make their travesty complete so flexible branches covered with long thorns (commonly used in bundles for firewood) were plaited into the shape of a crown and pressed into Jesus’s scalp. Again, there was copious bleeding — the scalp being one of the most vascular areas of the body.
The Roman soldiers saw a great joke in this provincial Jew claiming to be king. They threw a robe across his shoulders and placed a stick in his hand for a scepter. They still needed a crown to make their travesty complete so flexible branches covered with long thorns (commonly used in bundles for firewood) were plaited into the shape of a crown and pressed into Jesus’s scalp. Again, there was copious bleeding — the scalp being one of the most vascular areas of the body.
After mocking Jesus and striking him across the face, the soldiers took the stick from his hand and struck him across the head, driving the thorns deeper into his scalp. Finally, they tired of their sadistic sport and the robe was torn from his back. Already having adhered to the clots of blood and serum in the wounds, its removal would have caused excruciating pain just as in the careless removal of a surgical bandage. It was almost as though Jesus were whipped again and the wounds once more began to bleed.
 In deference to Jewish custom, the Romans returned his garments. The heavy patibulum of the cross was tied across Jesus’s shoulders and the procession of the condemned Christ, two thieves, and the execution detail of Roman soldiers headed by a centurion began a slow journey along the Via Dolorosa.
In deference to Jewish custom, the Romans returned his garments. The heavy patibulum of the cross was tied across Jesus’s shoulders and the procession of the condemned Christ, two thieves, and the execution detail of Roman soldiers headed by a centurion began a slow journey along the Via Dolorosa.
In spite of Jesus’s efforts to walk erect, the weight of the heavy wooden beam, together with the shock produced by copious blood loss, would be too much. He stumbled and fell. The rough wood of the beam gouged into the lacerated skin and shoulder muscles. Jesus tried to rise but his human muscles were pushed beyond their endurance.
The centurion, anxious to get on with the crucifixion, selected a stalwart North African onlooker, Simon of Cyrene, to carry the cross. Jesus followed, still bleeding and sweating the cold, clammy sweat of shock until the 650-yard journey from the fortress Antonia to Golgotha was finally completed. Jesus was offered wine mixed with myrrh, a mild analgesic mixture. He refused to drink. Simon was ordered to place the patibulum on the ground and Jesus was quickly thrown backward with his shoulders against the wood.
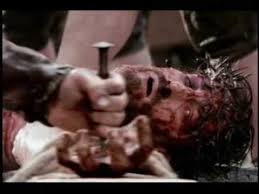 The legionnaire felt for the depression at the front of Jesus’s wrist. He drove a heavy, square, wrought-iron nail through the wrist and deep into the wood. Quickly, he moved to the other side and repeated the action, being careful not to pull his arms too tightly, but to allow some flexion and movement. The patibulum was then lifted in place at the top of the stipes and the titulus reading “Jesus of Nazareth, King of the Jews” was nailed in place.
The legionnaire felt for the depression at the front of Jesus’s wrist. He drove a heavy, square, wrought-iron nail through the wrist and deep into the wood. Quickly, he moved to the other side and repeated the action, being careful not to pull his arms too tightly, but to allow some flexion and movement. The patibulum was then lifted in place at the top of the stipes and the titulus reading “Jesus of Nazareth, King of the Jews” was nailed in place.
Jesus’s left foot was now pressed backward against his right foot and with both feet extended, toes down, a nail was driven through the arch of each, leaving his knees moderately flexed.
Jesus was now crucified.
As he slowly sagged down with more weight on the nails in the wrists, excruciating pain would have shot along Jesus’s fingers and up the arms to explode in the brain — the nails in the wrists putting pressure on the median nerves.
 Jesus would have pushed himself upward to avoid this stretching torment and he’d have placed his full weight on the nail through his feet. Again, there would be searing agony of the nail tearing through his nerves between the metatarsal bones of the feet. At this point, as his arms fatigued, great waves of cramps would have swept over Jesus’s muscles, knotting them in deep, relentless, throbbing pain. With these cramps would come the inability to push himself upward.
Jesus would have pushed himself upward to avoid this stretching torment and he’d have placed his full weight on the nail through his feet. Again, there would be searing agony of the nail tearing through his nerves between the metatarsal bones of the feet. At this point, as his arms fatigued, great waves of cramps would have swept over Jesus’s muscles, knotting them in deep, relentless, throbbing pain. With these cramps would come the inability to push himself upward.
Hanging by his arms, the pectoral muscles would be paralyzed and Jesus’s intercostal muscles would be unable to act.
As air could be drawn into the lungs but not exhaled in this position, Jesus would have fought to raise himself in order to get even one short breath. Finally, carbon dioxide would build up in his lungs and in the blood stream — the cramps would partially subside. Spasmodically, Jesus would push himself upward to exhale and bring in the life-giving oxygen.
 Jesus would have experienced several hours of limitless pain, cycles of twisting, joint-rending cramps, intermittent partial asphyxiation, and searing pain where tissue was torn from his lacerated back as he moved up and down against the rough timber.
Jesus would have experienced several hours of limitless pain, cycles of twisting, joint-rending cramps, intermittent partial asphyxiation, and searing pain where tissue was torn from his lacerated back as he moved up and down against the rough timber.
Then another agony began — a terrible crushing pain deep in the chest as Jesus’s pericardium slowly filled with serum and began to compress the heart.
This is documented in the 22nd Psalm, 14th verse: “I am poured out like water, and all my bones are out of joint; my heart is like wax; it is melted in the midst of my bowels.”
 It was now almost over. The loss of tissue fluids had reached a critical level — Jesus’s compressed heart struggling to pump heavy, thick, sluggish blood into the tissue — his tortured lungs making a frantic effort to gasp in small gulps of air — the markedly dehydrated tissues sending their flood of stimuli to his brain.
It was now almost over. The loss of tissue fluids had reached a critical level — Jesus’s compressed heart struggling to pump heavy, thick, sluggish blood into the tissue — his tortured lungs making a frantic effort to gasp in small gulps of air — the markedly dehydrated tissues sending their flood of stimuli to his brain.
Jesus gasped “I thirst.”
Another verse from the prophetic 22nd Psalm refers to this. “My strength is dried up like a potsherd; and my tongue cleaveth to my jaws; and thou has brought me into the dust of death.” A sponge soaked in posca, the cheap, sour wine which is the staple drink of the Roman legionaries, was lifted to his lips but Jesus apparently didn’t take any liquid.
 Jesus’s body was now in extremes — he would be able to feel the chill of death creeping through his tissues. This realization brought out his words, possibly little more than a tortured whisper. “It is finished.” Jesus’s mission of atonement was completed and, finally, he could allow his body to die. With one last surge of strength, Jesus would again press his torn feet against the nail, straighten his legs, take a deeper breath, and utter a last cry. “Father! Into thy hands I commit my spirit.”
Jesus’s body was now in extremes — he would be able to feel the chill of death creeping through his tissues. This realization brought out his words, possibly little more than a tortured whisper. “It is finished.” Jesus’s mission of atonement was completed and, finally, he could allow his body to die. With one last surge of strength, Jesus would again press his torn feet against the nail, straighten his legs, take a deeper breath, and utter a last cry. “Father! Into thy hands I commit my spirit.”
In order that the Sabbath not be profaned, the Jews asked that the condemned men be dispatched and removed from the crosses. The common method of ending a crucifixion was by crurifracture — the breaking of the leg bones. This prevented the victim from pushing himself upward — the tension could not be relieved from the muscles of the chest and rapid suffocation occurred. The legs of the two thieves were broken but when the soldiers came to Jesus they saw this was unnecessary.
Apparently, to make doubly sure of death, the legionnaire drove his lance through the fifth interspace between Jesus’s ribs — upward through the pericardium and into the heart.
 The 34th verse of the 19th chapter of the Gospel according to St. John reports, “And immediately there came out blood and water.” That is, there was an escape of watery fluid from the sac surrounding the heart. This is solid postmortem evidence that Jesus died not the usual crucifixion death by suffocation. The actual anatomical cause of Jesus Christ’s death was heart failure due to shock and constriction of the heart by fluid in the pericardium.
The 34th verse of the 19th chapter of the Gospel according to St. John reports, “And immediately there came out blood and water.” That is, there was an escape of watery fluid from the sac surrounding the heart. This is solid postmortem evidence that Jesus died not the usual crucifixion death by suffocation. The actual anatomical cause of Jesus Christ’s death was heart failure due to shock and constriction of the heart by fluid in the pericardium.
This is our glimpse — including the medical evidence — of that epitome of evil that man has exhibited toward man and toward God.
* * *
 When there’s a wreck on the side of the road, we can’t help it. Despite our best efforts, we look at the accident, sometimes even slow down to get a really good look.
When there’s a wreck on the side of the road, we can’t help it. Despite our best efforts, we look at the accident, sometimes even slow down to get a really good look. Often, though, we do precisely the opposite when it comes to the apparently unfixable, to the enormity of horrible events, to tragedies. (Enormity doesn’t mean “extra enormous.” It refers to the emptiness of something so horrible and large we have trouble comprehending it).
Often, though, we do precisely the opposite when it comes to the apparently unfixable, to the enormity of horrible events, to tragedies. (Enormity doesn’t mean “extra enormous.” It refers to the emptiness of something so horrible and large we have trouble comprehending it). There’s a long history of denialism, defending the status quo and ignoring what others discover. That two balls of different weights fall at the same speed. That the Earth rotates around the Sun. That the world is millions of years old. That we walked on the Moon. The denials all sound the same. They don’t come from stupidity, from people who aren’t smart enough to understand what’s going on. They come from people who won’t look.
There’s a long history of denialism, defending the status quo and ignoring what others discover. That two balls of different weights fall at the same speed. That the Earth rotates around the Sun. That the world is millions of years old. That we walked on the Moon. The denials all sound the same. They don’t come from stupidity, from people who aren’t smart enough to understand what’s going on. They come from people who won’t look. What happens to one’s standing when you dare to question the accepted status quo? What are the risks to doing your own research, to putting forth a falsifiable theory and being prepared to find it proven wrong? What will you tell your neighbours?
What happens to one’s standing when you dare to question the accepted status quo? What are the risks to doing your own research, to putting forth a falsifiable theory and being prepared to find it proven wrong? What will you tell your neighbours?



























