Personal DNA testing is a huge business. Genetic profiling on an individual or home-based level is a multi-million dollar industry that’s tripling each year. As the biological identification process becomes faster, easier and cheaper, more and more people are submitting their spit. What they’re finding can be fascinating—or terrifying—which makes some folks reluctant to try. But, if you’re curious about checking out your molecular makeup, here’s what you need to know about personal DNA testing.
Personal DNA testing is a huge business. Genetic profiling on an individual or home-based level is a multi-million dollar industry that’s tripling each year. As the biological identification process becomes faster, easier and cheaper, more and more people are submitting their spit. What they’re finding can be fascinating—or terrifying—which makes some folks reluctant to try. But, if you’re curious about checking out your molecular makeup, here’s what you need to know about personal DNA testing.
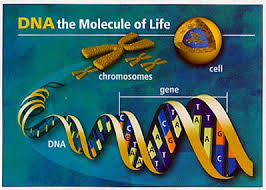
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It’s the basic building block of organic life—the blueprint prescribing every bit of non-local as well as tangible information required to make a bee a bee, a bird a bird, and a beluga a beluga. DNA is also what makes you… you.
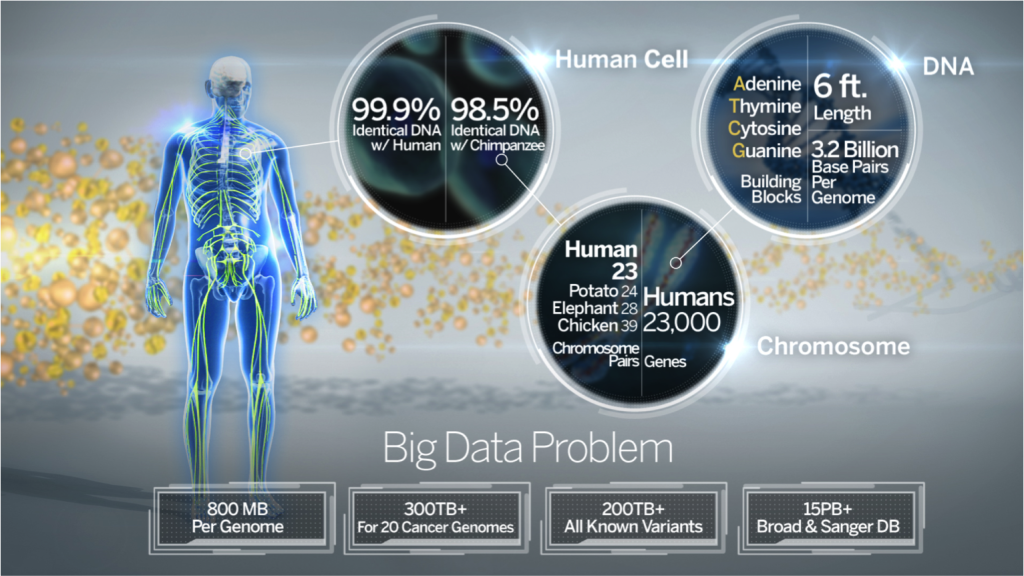
About 99 percent of your DNA is universal to the living world. You share most of the same biological codes with other carbon-based life forms. As you move closer to your mammalian cousins like the apes or the now-extinct Neanderthals, that 1 percent of your human coding narrows. By the time you reach your individual family level, DNA gets very unique.
Your personal DNA profile is as individual to you as your fingerprints. That’s unless you have an identical or monozygotic twin, in which case you’d have the same genetic blueprint. Or, you might be an exceptionally rare occurrence known as a chimera. In that event, you’d have two different DNA profiles within your cells.
How DNA Operates in Human Cells
 Cells allow you to be a living human. Every part of you, from your blood to your bones to your brain, is made of individual cells. There’s no way to count the number of cells in your body as they’re constantly changing. You have more cells as you grow from a toddler to a teen and less cell material when you succeed on your diet.
Cells allow you to be a living human. Every part of you, from your blood to your bones to your brain, is made of individual cells. There’s no way to count the number of cells in your body as they’re constantly changing. You have more cells as you grow from a toddler to a teen and less cell material when you succeed on your diet.
It’s estimated the human body, like yours, completely recreates itself every month or so. New cells replace your old cells and life goes on until you die. Then your cells stop reproducing, and you begin decomposing which is an entire science of its own.
The amazing thing about your cell regeneration is that, for the most part, they perfectly reproduce. That’s thanks to the specific information encoded in your DNA. Without DNA direction, you’d be like trying to repeatedly rebuild the space station without the plans.
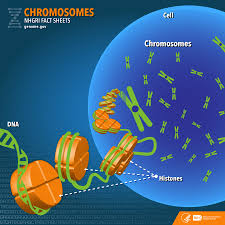 What makes you unique as a human being, rather than an ape, is your chromosomes. These are particular chapters in your DNA playbook and appear as lengths of information in your genome sequence. As humans, we have 22 pairs of chromosomes that direct everything from skin color to disease resistance. It’s problems with information breakdown in chromosomes that are leading causes of birth defects and inherited disorders.
What makes you unique as a human being, rather than an ape, is your chromosomes. These are particular chapters in your DNA playbook and appear as lengths of information in your genome sequence. As humans, we have 22 pairs of chromosomes that direct everything from skin color to disease resistance. It’s problems with information breakdown in chromosomes that are leading causes of birth defects and inherited disorders.
There’s a distinct difference in boys and girls and women and men. That’s because of the 23rd pair of chromosomes that complete our human makeup. All females have two X-chromosomes in their last pair while males have one X chromosome complimented with a single Y-chromosome. Genetically, female chromosome equations get expressed as 22+XX while males are 22+XY.
The numbers associated with the human genome project, and where DNA fits in, are truly staggering. It’s a wonder we function at all. There are four biological building blocks in your DNA which are nucleotide chemical bases—adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). You have approximately 3.2 billion pairs of A, T, C and G in your cellular makeup. That’s a total of 6.4 billion letters describing your DNA genome code which contains 6,500 segments known as centimorgans (cM). Multiply this by the trillions of cells in your body…
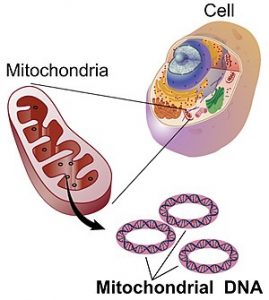
 You actually have two DNA types active in your cells. One is “regular” deoxyribonucleic acid that supplies codes for building physical cell structure. The other is mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (mtDNA). The mitochondrion is a human cell component that creates energy. Each cell contains 16,569 base pairs of mtDNA.
You actually have two DNA types active in your cells. One is “regular” deoxyribonucleic acid that supplies codes for building physical cell structure. The other is mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (mtDNA). The mitochondrion is a human cell component that creates energy. Each cell contains 16,569 base pairs of mtDNA.
Mitochondrial DNA is Maternal
You get mitochondrial DNA from your mother who got your genetic recipe from your grandmother. It’s a unique biological occurrence that happens on your maternal side and geneticists believe it’s because the pre-fertilized egg that you started from needed an energy source and coding to initially program it. From the point of conception, when your father’s sperm joined your mother’s egg and created you as a zygote before you were an embryo (Google it – zygote is a freshly fertilized egg), your cell nucleus information remained maternally bound.
 Mitochondrial DNA has nothing to do with determining chromosomes and whether you turned out male or female. Having two XXs or a Y and an X was a biological crapshoot. It’s a flip of the coin, according to theory, and it’s amazing that after the billions and billions of babies born, they average about 51 percent female and 49 percent male. Go figure who figured the odds.
Mitochondrial DNA has nothing to do with determining chromosomes and whether you turned out male or female. Having two XXs or a Y and an X was a biological crapshoot. It’s a flip of the coin, according to theory, and it’s amazing that after the billions and billions of babies born, they average about 51 percent female and 49 percent male. Go figure who figured the odds.
But your chromosomes, directed by your regular DNA and powered by your mtDNA have everything to do with how you turned out. Some speculate DNA contributes to how you act and feel, as well. Although there’s no scientific proof of DNA contributing to emotions, let alone consciousness, it’s because of DNA that we’re alive and curious. One of the biggest curiosities today is what our DNA profile tells us about who we are and where we came from. Perhaps it’s that knowledge that helps us understand where we’re going.
How Personal DNA Testing Happens
An internet search finds over twenty outlets offering personal DNA profiling services. Some are credible. Some are not. It’s caveat emptor in the profiling business and we’ll cover that in a bit. First, let’s look at how a typical DNA profile happens. It goes like this:
Research the Service and Provider Best Suited to Your Goal
That might be tracing your ancestry, determining parentage, finding relatives, planning a family, identifying genetic risk through inherited deficiencies, determining pharmacological compatibility, developing a lifestyle or any one of a number of motives for why you’d want to see your profile. Be cautious, though, of relying on dubious predictions on optimal diets and such. Experts warn that using DNA tests to extrapolate this type of information is probably pseudoscience.
Order Your Collection Kit Online
Most companies now use sterile swabs for collecting saliva. Good old spit is by far the best-suited substance for DNA typing. Sure, the forensic scientists can isolate DNA from blood, bone marrow, hair follicles, semen samples, vaginal fluid and mucus. But, for obvious reasons, these aren’t best managed for a personal collection.
Collect Your Saliva Sample
Your mouth is full of genetic material. By far the best area of your mouth to swab is your inner cheek or under your tongue where you store the largest amount of buccal swabs. Some companies supply tubes to simply spit into, but the most efficient and accurate collection method is swabbing. At any rate, you can’t go wrong by following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Package Your Sample
Your kit provider will include a vial to seal your swab and prevent contamination. Cross-contamination can ruin a personal DNA test, so make sure you have limited handling and that you keep others some distance from your swabbing. The return envelope or container should be pre-addressed and suitable for regular mail. You might have to buck-up for postage, depending on who’s doing your test.
Register Your Sample
This is extremely important. All DNA testing companies require online registering before they receive your swab. Otherwise, they can’t process it. Again, follow the directions and select your options. Some testing agencies require completed questionnaires. If you have privacy concerns, it’s best to read the fine print or call their customer service line.
Wait for Your Results
You’ll have to wait anywhere from four to eight weeks to receive your DNA profiling results. This depends on the particular company, their backlog and how detailed an analysis you requested. You’ll be digitally notified, likely by email, or you may have to log on to your private portal.
Decipher Your Personal DNA Test
This might be the most difficult part of your whole DNA profile procedure. If you’re simply looking for ancestry information, it might be straightforward. But, if you’ve ordered an in-depth search into your maternal or paternal lineage, there’ll be more to it. That’s certainly so if you’ve requested genetic information pertaining to your health.
Available DNA Testing Services for Individuals
There are three main DNA testing services available for personal profiling. Keep in mind that you’re dealing with a civilian process that’s an interesting information exercise rather than a forensic examination bound by the rules of evidence. Civilian genetic testing agencies will offer one or all of these services:
Autosomal Testing — This is the most basic and popular means of genetic testing. It’s commonly called the family finder. The autosomal method looks at your 22 standard chromosome pairs, not including the ones that determine your sex. The first 22 chromosome pairs are called autosomes. Through autosomal typing, the service aligns you with other profiles already stored in their database and matches you with similar people. As regular DNA changes with generations, autosomal testing only goes back 5-8 generations, unlike the other two services that can profile you between 20 and 100 generations.
mtDNA Testing — Mitochondrial services focus on the X chromosome in your DNA profile. Every human has an X chromosome signature regardless if they’re female or male. mtDNA profiling is precise and this is where geneticists zero-in on abnormalities in your traits and indicate issues that you’d otherwise have no idea about.
Y-DNA Testing — This one’s for boys only. As women don’t have a Y chromosome, they can’t play this game. Y-DNA testing follows the paternal line that’s passed from fathers to sons. However, don’t write-off the girls too quick. They have a way around determining their paternal line. If you’re female, you can simply ask your biological brother for a Y-DNA test and you’ll find all about your dad’s side of the family.
How the Science of Personal DNA Testing Works
 There’s nothing simple about DNA testing science. This is a highly-trained, exacting discipline done in expensive laboratory environments. As with other science arenas, DNA testing methods have rapidly improved with technology. Today, scientists can extract the smallest DNA fragment and multiply it as many times as necessary to develop an accurate profile. It’s like cloning.
There’s nothing simple about DNA testing science. This is a highly-trained, exacting discipline done in expensive laboratory environments. As with other science arenas, DNA testing methods have rapidly improved with technology. Today, scientists can extract the smallest DNA fragment and multiply it as many times as necessary to develop an accurate profile. It’s like cloning.
Once your saliva sample hits the lab, technicians extract your DNA content from the liquid through a centrifuge and plating procedure. What they’re looking for is an area of your genome sequence that displays certain variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs). Within the identified VNTR points are smaller sections called short tandem repeats (STRs) which are microsatellites that really tell the story of who you are, who made you and where you came from.
 You’ll find a lot of DNA lingo if you surf the net. Some terms are PCR, RFLP and ALFP but the only notable acronym that applies to personal testing is STR. From STR information, technicians apply a quantitative analysis that provides a statistical interpretation of approximately 20 “loci” core markers. This is as technical as you need to get in order to understand what’s happening with your spit at the shop.
You’ll find a lot of DNA lingo if you surf the net. Some terms are PCR, RFLP and ALFP but the only notable acronym that applies to personal testing is STR. From STR information, technicians apply a quantitative analysis that provides a statistical interpretation of approximately 20 “loci” core markers. This is as technical as you need to get in order to understand what’s happening with your spit at the shop.
It’s the power of statistical discrimination that’s amazing in STR DNA analysis. You’ll hear DNA technicians speak of statistical probabilities when quantifying the reliability and accuracy of your DNA test. It’s common to hear results like 99.999 percent or one-in-a-billion. No matter how they present your results, you still have to do some interpretation.
Commercial Services for Personal DNA Testing
No doubt you were waiting for this part. Now that you have some idea of what personal DNA testing entails and are taking the plunge into the biological soup-pot that supports you, the question is what services are suitable for you. In other words, what’s the best bang for your biological buck?
 Well, this website isn’t associated with commercial DNA testing and receives no referral fee, so there’s every reason to be independently objective. There are plenty of providers and gobs of internet information available, so you’ll have to do a bit of homework. To help you speed the process, here are the highest rated commercial services for personal DNA testing:
Well, this website isn’t associated with commercial DNA testing and receives no referral fee, so there’s every reason to be independently objective. There are plenty of providers and gobs of internet information available, so you’ll have to do a bit of homework. To help you speed the process, here are the highest rated commercial services for personal DNA testing:
Cellular Research Institute (CRI) — This seems to be the Cadillac of DNA testing services, according to Genetics Digest. It also seems to be the only one employing a world-renown, Harvard-educated genetic scientist who trained under Dr. Watson (who is one of the co-discoverers of the DNA double-helix molecule). CRI has an amazing depth of analysis and a widely expanding database. They’re not expensive, though, considering what you get. You can pay $99 for a quick ancestry test and $199 for a basic ancestry & heath profile. The price quickly rises for specialized work.
AncestryDNA — These DNA testers are probably the best known providers. That’s because they’ve been around the longest after starting Ancestry.com. Originally, Ancestry was an online family tree service. They got into the DNA business as a value-added service and are highly reputable. Ancestry is also relatively affordable. Prices start at $129 and go to $299, depending on what service you want.
23and Me — If you’re looking for thorough ancestor reports and some decent health observations, 23andMe is a good choice. They’re fairly new and their marketing really appeals to millennials. So does their price point. 23andMe has an a la carte menu starting at $99.
tellmeGen — If you’re a hypochondriac, you’ll want to pick up a tellmeGen personal DNA testing kit. They do basic autosomal tests, but really shine when drilling down into what’s behind your health concerns (real and imaginary). You’ll pay for it, though, as their entry level test is $169 and it climbs from there.
MyHeritage — For basic, bottom-line DNA testing on a budget watch, get yourself a kit from MyHeritage. You’ll shell out $109 and they’ll be back to you in 3-4 weeks with a really cool pie-chart of what’s going on in your body.
Remember Caveat Emptor
 In personal DNA testing—like most things in life—you get what you pay for. Good services cost money and, if you want credible results, you’ll have to buck-up. That’s not to say that many other commercial DNA services aren’t honorable, credible and valuable. A quick internet scan finds agencies like LivingDNA, FamilyTreeDNA, AfricanAncestry and even National Geographic Geno 2.0. They’re probably fine, too.
In personal DNA testing—like most things in life—you get what you pay for. Good services cost money and, if you want credible results, you’ll have to buck-up. That’s not to say that many other commercial DNA services aren’t honorable, credible and valuable. A quick internet scan finds agencies like LivingDNA, FamilyTreeDNA, AfricanAncestry and even National Geographic Geno 2.0. They’re probably fine, too.
But you will find some scammers. One online investigator submitted saliva from his golden retriever, Bailey. He got back a computer generated profile that missed Bailey’s species but got her hair color right. The report also profiled Bailey as not suitable for contact sports and suggested she take up golf.