A conspiracy theory is the belief that a plot by powerful people or an organization is working to accomplish a sinister goal—the truth of its existence secretly held from the public. Conspiracy theorists see authorities—governments, corporations, and wealthy people—as fundamentally deceptive and corrupt. Their distrust of official narratives runs so deep that they connect dots of random events into what they believe make meaningful patterns, despite overwhelming conflicting evidence, or absence of supporting evidence, to their conclusions. Aside from a lack of reason and common sense, what makes crazy conspiracy theorists tick?
A conspiracy theory is the belief that a plot by powerful people or an organization is working to accomplish a sinister goal—the truth of its existence secretly held from the public. Conspiracy theorists see authorities—governments, corporations, and wealthy people—as fundamentally deceptive and corrupt. Their distrust of official narratives runs so deep that they connect dots of random events into what they believe make meaningful patterns, despite overwhelming conflicting evidence, or absence of supporting evidence, to their conclusions. Aside from a lack of reason and common sense, what makes crazy conspiracy theorists tick?
First, let’s look at what Time Magazine identified as the prominent conspiracy theories believed by the American public. These were identified in a recent poll, and I’m not kidding you. Some people actually swallow these kooky concoctions.
From lowest to highest percentage, they are:
10. The Reptile Elite — Among us are flesh-eating, blood-drinking, shapeshifting, extraterrestrial reptilian humanoids bent on enslaving the human race. The British Royals and the Bush family are part of the group, as was Margaret Thatcher.
9. The CIA and AIDS — Thinking is that the Central Intelligence Agency was out to destroy homosexuals and blacks, so they invented the deadly HIV virus and injected it in place of hepatitis vaccinations.
8. Holocaust Revisionism — Most deniers accept that the internment camps existed but claim the numbers of people murdered are greatly exaggerated. General Eisenhower saw this coming when he forced hundreds of civilian witnesses to tour the camps and bear the truth to the world.
7. Jesus and Mary Magdalene — These folks claim Jesus and Mary Magdalene were a married couple, but Jesus occasionally shared her with his disciple, Peter. They attribute this to the Gnostic Gospels which were discovered in 1945 and claim it’s being covered up by the Vatican. Mainstream scholars dismiss as the Gnostic Gospels as even being authentic.
6. The Moon Landings Were Faked — According to this crowd, none of the Apollo missions happened. They were filmed on a Hollywood lot, or possibly at area 51. Watch this priceless clip of Buzz Aldrin punching conspiracy theorist Bart Sibrel in the face. Click Here
5. Secret Societies Rule the World — If you’re a member of the global elite, then you’d already know this. And you might belong to one or more of many groups; the Illuminati, Freemasons, Skull & Bones, Opus Dei, Bilderberg Group, or maybe even have a seat on the Council of Foreign Relationship. Sorry, your Costco card won’t cut it.
4. Paul McCartney is Dead — Supposedly the Beatles covered-up the real Sir Paul’s death in 1966 and an imposter has been in his place ever since. Maybe I’m Amazed, because I saw a recent clip of Paul McCartney in front of tens of thousands at Hyde Park takin’ a swing at Pretty Woman with Bruce Springsteen. If he’s an imposter, he’s some good at it.
3. Area 51 and Aliens — There’s a real Air Force base at Groom Lake, 150 miles north of Las Vegas, where all sorts of black op aircraft are tested. Like most military installations, public access is restricted, but you can get a good look at it on Google Earth. The resolution is excellent, but I couldn’t find any saucer-shaped craft or ET-looking creatures. Oh, right… they keep them inside… or maybe back at Roswell.
2. 9/11 Cover-Up — Apparently 42% of Americans believe the attacks on the New York, Washington, and Pennsylvania were orchestrated by some arm of the U.S. Government. Sad.
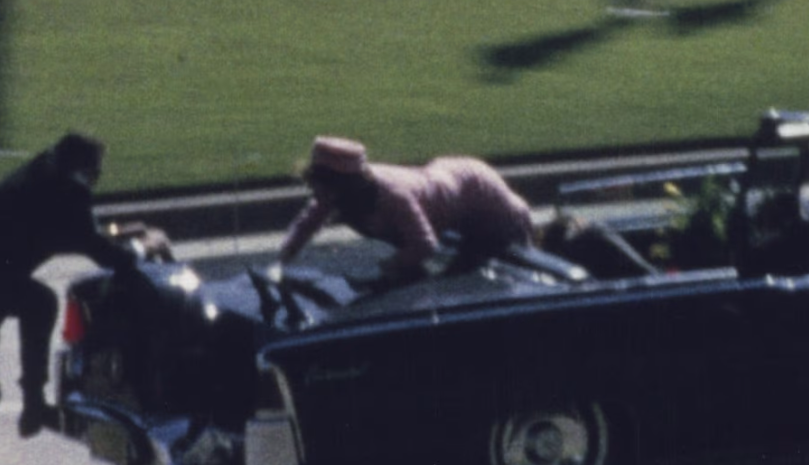
1. The JFK Assassination — The mother of conspiracy theories. Times’ poll reports that only 32% believe that Lee Harvey Oswald acted alone. So, two-thirds of Americans truly think their 35th President’s murder is unsolved? How can that be?
Well, it comes down to mindset.
I’m not saying that conspiracies don’t happen—even at a mass scale. The Holocaust was a massive conspiracy to exterminate the Jews. The Nazis totally believed the Jews were a threat to their existence. It was an article of faith within the Third Reich.
 9/11 was a monstrous conspiracy—orchestrated by Bin Laden and al-Qaeda. The Russian Revolution was a conspiracy. So was the American Revolution—fifty-six men signed the Declaration of Independence. Nixon conspired to hide Watergate. Abraham Lincoln was murdered through a conspiracy. So was Julius Caesar. Don’t forget Stalin, the Mexican Drug Cartels, and Scientology. And don’t get me going on Klaus Schwab with his Fourth Industrial Revolution, Davos, and the World Economic Forum.
9/11 was a monstrous conspiracy—orchestrated by Bin Laden and al-Qaeda. The Russian Revolution was a conspiracy. So was the American Revolution—fifty-six men signed the Declaration of Independence. Nixon conspired to hide Watergate. Abraham Lincoln was murdered through a conspiracy. So was Julius Caesar. Don’t forget Stalin, the Mexican Drug Cartels, and Scientology. And don’t get me going on Klaus Schwab with his Fourth Industrial Revolution, Davos, and the World Economic Forum.
If some conspiracies are true, then how do you determine which ones are false? The more these characteristics apply, the more likely the theory is wrong:
- “Proof” of the conspiracy emerges through dot-connecting without any hard, physical evidence.
- Execution requires large and complex elements.
- The agents require nearly super-human powers.
- Everyone maintains secrecy.
- There is a grandiose ambition for control.
- The plot ratchets from small to large events.
- Everything has a sinister overtone.
- Facts and speculation are mingled without assigning degrees of probability.
- The theorist is extremely suspicious of authority—government and private.
- The theorist refuses to consider alternative explanations, seeking only confirmation of the theory.
I understand the mindset of real conspirators. It’s all about money, power, and/or self-preservation. But what about the tin-foil hat crowd?
In American Conspiracy Theories, political scientists Joseph Uscinski and Joseph Parent conducted an “extensive empirical study” on the subject and found: Conspiracy Theorists are often caricatured as a small demographic composed primarily of middle-aged white male internet enthusiasts who live in their mother’s basements—but that’s wrong. Conspiracy theories permeate all parts of society and cut across age, gender, race, income, political affiliation, educational level, and occupational status.
What gives? How does a cross-section of should-be normal people get so distorted in their thoughts and believe in really weird things?
Quassim Cassam, who published a peer-reviewed paper title Conspiracy Theories, is a professor of philosophy at the University of Warwick. He’s embarking on a study on why people believe in outlandish theories. Part of this work is to answer why people get pushed to extremes like joining ISIS.
Professor Cassam says: It seems to be because of the kind of thinker they are, or to put it bluntly, because there’s something wrong with how they think. It’s the peculiarities of their intellectual constitution—in a word, their intellectual character. It’s what social psychologists call a conspiracy mentality.
Cassam goes on: The gullible rarely believe they’re gullible and the closed-minded don’t believe they’re closed-minded. Closed-mindedness is the toughest intellectual vice to tackle because it’s in its very nature to be concealed from those who have it. There’s no reasoning with those kinds of people.
I found an article in Sage Journals where Willem van Prooijen of the University of Amsterdam summed it: Conspiracy theorists tend to have one thing in common—they feel a lack of control over their lives.
Some DyingWords followers know I’m a life-long student of the John F Kennedy Assassination, and I’m completely satisfied beyond all doubt that Lee Harvey Oswald did it—acting alone. Part of my research was checking online chat boards on the JFK forums. Lemme tell you—there are some whacko, nut-jobs out there. One of them made repeated death threats to me via email for calling out BS in the JFK CT department.
I believe there are four reasons why people believe JFK’s murder was a conspiracy. These reasons probably apply to most conspiracy theories and theorists.
1. They don’t have the correct information to understand the case facts.
2. They haven’t got the personal knowledge, or experience, to properly interpret the evidence.
3. They simply want to believe in a conspiracy.
4, They don’t have the mental capacity for critical thought process.
Professor Cassam is right. There’s no reasoning with those kinds of people.