Is there life after death? That’s a question folks have asked since the dawn of humanity. Historically, the answer has been faith-based. But today, modern science is closer to the truth following a major medical discovery at the University of Michigan. However, it depends on what your definition of life is. And your definition of death.
Is there life after death? That’s a question folks have asked since the dawn of humanity. Historically, the answer has been faith-based. But today, modern science is closer to the truth following a major medical discovery at the University of Michigan. However, it depends on what your definition of life is. And your definition of death.
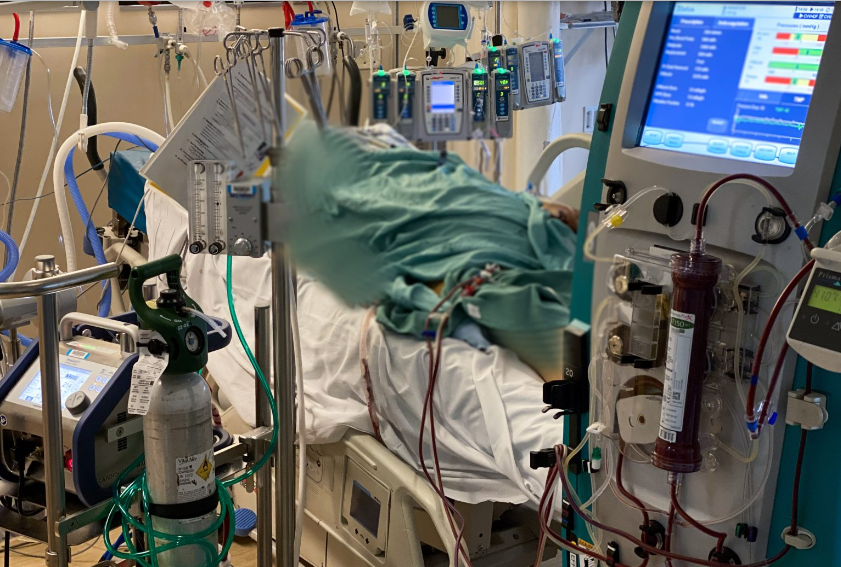
In 2014, a 24-year-old woman collapsed at home. She was taken to Emergency at U of M medical center where staff were unable to regain her consciousness. They moved her to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), and she remained in ICU for four days while hooked to an electroencephalograph (EEG) to monitor her brain function. It showed she was in “brain death”.
Despite being on organic life support, (heart-lung machine) she flatlined on the electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor and went into cardiac arrest with her respiration ceasing — “clinical death” as it’s commonly called. Because her physical death seemed inevitable during the four days, her family had signed a Do Not Resuscitate (DNR) order. The woman remained in her bed, not breathing nor beating, and was still connected to the EEG for some time before she was removed to the morgue.
That was the end of this woman’s bodily life. Her physical life. But it wasn’t the end of her conscious life. In 2022, a researcher at the U of M reviewed the woman’s EEG charts and found that, astonishingly, at the moment of clinical death the woman’s brain came back to life—in fact into a hyperdrive in activity in the regions associated with consciousness. According to the researcher, “Something happened in that brain that makes no sense at all.”
We’ll closely examine what took place in that ward where Patient One, as she’s now known in the medical research community, physically passed away. And we’ll look at what consciousness, as that term applies to living human beings, might be. First, let’s review the definitions of death as they apply to clinical death and brain death, which are two separate deals. And see if it’s time for a new science of death.
I found a great death explanation resource at the United States National Library of Medicine. At their National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) section there’s a multi-part series, one of which is titled Definitions of Death: What and When is Death? Interestingly, they divide it into two aspects. One is biological death. The other is social death.
To quote them. “The commonplace notion of death is to characterize it as an end state: being dead. Nevertheless, being dead is not the same as the event of death or the dying process.
Biological death can be understood as:
- A final event.
- An absolute state: being dead.
- Part of the dying process.
The absolute state of being dead is synonymous with the idea of medical or clinical death—where an individual has sustained irreversible cessation of circulatory and respiratory functions or irreversible cessation of all functions of the entire brain, including the brain stem.
Social death is a relational change in the meaning of a human life. It involves a change in the narrative identity of persons that either still biologically exist or have once existed.”
Biological death and social death, as set out in the NCBI paper, is broader coverage than what’s usually weighed in the mainstream medical community, such as physicians and coroners would use. From my experience in the death investigation business, we almost always relied on the clinical death measurement rather than the brain death evaluation. That’s because very few deaths are recorded on EEGs, and there is no brain activity to monitor. Therefore, the declaration of death usually refers to the standard definition of clinical death which is:
The cessation of blood circulation and breathing; the two criteria necessary to sustain human life.
Brain death is a different matter—the classic definition being:
The complete and irreversible loss of brain function to the point where there is no return.
So, is it possible to be dead and alive at the same time? Apparently, yes, as in the case of Patient One whose circumstances we’ll examine shortly. Before that, let’s look at the Florida Boy case as reported in the NCBI literature.
Florida Boy is a legal precedent of a boy who spent 14 years in an ICU connected to a heart-lung machine after an initial diagnosis of complete and total brain failure. He showed no EEG activity at all during that time. His parents demanded that he be artificially ventilated, fed, and hydrated in the hospital.
Over the 14 years, the boy biologically grew into a man as if he were normal—except in total death as in any form of consciousness. Interestingly, as his thorax and abdomen organ cellular activity functioned normally, his brain cells gradually replaced themselves and became a “grey goo of ghost-like tissues”. Apparently, without brain activity, the entire cerebral system decomposes. Not so with the neck-down region. The boy-turned-man was eventually disconnected via a court order, and he completed his clinical death cycle.
Let’s return to Patient One. Dr. Jimo Borjigin is a professor of neurology at the University of Michigan. As a project of interest, she investigated reports of Near Death Experiences (NDE) reported by resuscitated patients. Her studies expanded into those who were officially ‘brain dead” as in EEG monitored while still clinically alive. She stumbled upon the Patient One records and found an anomaly never before seen in medical experience.
Here’s Dr. Borjigin’s account:
— —
In the moments after Patient One was taken off oxygen, there was a surge of activity in her dying brain. Areas that had been nearly silent while she was on life support suddenly thrummed with high-frequency electrical signals called gamma waves. In particular, the parts of the brain that scientists consider a “hot zone” for consciousness became dramatically alive. In one section, the signals remained detectable for more than six minutes. In another, they were 11 to 12 times higher than they had been before Patient One’s ventilator was removed.
As she clinically died, Patient One’s brain was functioning in a kind of hyperdrive. For about two minutes after her oxygen was cut off, there was an intense synchronization of her brain waves, a state associated with many cognitive functions, including heightened attention and memory. The synchronization dampened for about 18 seconds, then intensified again for more than four minutes. It faded for a minute, then came back for a third time.
In those same periods of dying, different parts of Patient One’s brain were suddenly in close communication with each other. The most intense connections started immediately after her oxygen stopped and lasted for nearly four minutes. There was another burst of connectivity more than five minutes and 20 seconds after she was taken off life support.
In particular, areas of her brain associated with processing conscious experience—areas that are active when we move through the waking world, and when we have vivid dreams—were communicating with those involved in memory formation. So were parts of the brain associated with empathy. Even as she slipped irrevocably deeper into death, something that looked astonishingly like life was taking place over many minutes in Patient One’s brain.
Those glimmers and flashes of something like life contradict the expectations of almost everyone working in the field of resuscitation science and near-death studies. The predominant belief—expressed by Greyson, the psychiatrist and co-founder of the International Association of Near Death Studies, in the Netflix series Surviving Death—was that as soon as oxygen stops going to the brain, neurological activity falls precipitously. Although a few earlier instances of slight and fading brain waves had been reported in dying human brains, nothing as detailed and complex as what occurred in Patient One had ever been detected.
Given the levels of activity and connectivity in particular regions of her dying brain, I believe it’s likely that Patient One had a profound near-death experience with many of its major features: out-of-body sensations, visions of light, feelings of joy or serenity, and moral re-evaluations of one’s life. Of course, Patient One did not recover, so no one can prove that the extraordinary happenings in her dying brain had experiential counterparts.
— —
Near Death Experiences. NDEs. Are these events of total imagination? Or are they completely real?
We’ve all heard the stories—the familiar kitsches of NDEs. Being elevated from the operating table. Floating toward an immense light. Traveling down a tunnel. Complete bliss and harmony. Being beckoned by an infinite intelligence. Meeting dead relatives. And not wanting to return to normal life.
While these NDE experiences can be simulated by taking a hero’s worth of ketamine, almost all reports come from rational and sober people who clearly felt they went through something extraordinary. Some say paranormal. Others say supernatural.
This brings us to that mysterious and mostly unknown subject of consciousness. Almost nothing is solidly understood about what consciousness really is. Partly, that’s because no one has found a way to isolate and measure consciousness—it’s very difficult (almost impossible) to fund studies that can’t be isolated and measured.
Dr. David Chalmers is a world-leading consciousness researcher. (I wrote a blog post on Chalmers and his consciousness theories a few years ago. You can read it here.) Dr. Chalmers posits that consciousness may be a fundamental property of the human brain and that consciousness may be a universal entity of the cosmos that sends signals to us. Chalmers breaks consciousness into two arenas—the easy problem of recognizing that it exists and the hard problem of explaining how it operates. Or what it is.
All of us experience at least two consciousness forms. One is our awake state, which you’re in at the present. The other is our asleep state, also known as the subconscious. As long as we’re “alive”, both states exist and are vital to our function and survival.
So, what gives with someone like Patient One? Why was she clinically dead—according to the standard description—after she flatlined in the ICU—yet came fully alive in her once-thought-dead brain? The answer seems to be that death, clinical and brain, is not a precise time point. Rather, both are processes that can take extensive linear time to complete.
There are countless stories of people being resuscitated minutes and even hours after their hearts stopped beating and their lungs stopped breathing. Many events occurred in hypothermic conditions; temperature being a huge life-preservation factor. But bringing someone back from brain death? It’s never been recorded before Dr. Borjigin stumbled upon Patient One’s charts.
This seems to be because no one has looked at this angle before. Once a patient flatlines in a medical environment and there’s no resuscitation made, there’s no reason to review the EEG charts—if there even are recordings. It’s just shut things down, shroud them, send them downstairs, and move on to the next.
Makes me wonder how many people are written off for dead when they’re still very much alive.
Maybe it’s time for a new science of death.