There’s something terrifying—absolutely horrific—about being axed to death. Hollywood’s made a killing off movies like The Shining, American Psycho, and So I Married An Ax-Murderer, not to mention Lord Of The Rings where Gimley, the ginger-bearded psycho-dwarf, double-blades dozens of ornery Orks. But movies aren’t real—not real life, that is. In reality, ax-murder victims don’t get up to act another day. I’ve investigated a few real-life ax-murders in my time, including one gruesome and grotesque axing scene that tops anything Hollywood has yet to script.
There’s something terrifying—absolutely horrific—about being axed to death. Hollywood’s made a killing off movies like The Shining, American Psycho, and So I Married An Ax-Murderer, not to mention Lord Of The Rings where Gimley, the ginger-bearded psycho-dwarf, double-blades dozens of ornery Orks. But movies aren’t real—not real life, that is. In reality, ax-murder victims don’t get up to act another day. I’ve investigated a few real-life ax-murders in my time, including one gruesome and grotesque axing scene that tops anything Hollywood has yet to script.
In fact, I’m just about finished the manuscript for In The Attic. It’s based on a true double ax-murder story and I’ll tell you what happened in that bedroom… eight feet below the attic. But first, let’s look at some other famous ax-murders that compete with my case.
15. The Axman of New Orleans
 Between May, 1918 and October, 1919 six men and six women were attacked in their Lower Ward homes and hacked to death with an ax. The MO was consistent. The killer knew when the victims were vulnerable. Entry was made through the back door. There were no sexual overtones, no evidence of robbery, and a common denominator was that all victims were Caucasian and mostly from Italian-American heritage. The series of killings stopped as abruptly as they started and no viable suspect was ever developed.
Between May, 1918 and October, 1919 six men and six women were attacked in their Lower Ward homes and hacked to death with an ax. The MO was consistent. The killer knew when the victims were vulnerable. Entry was made through the back door. There were no sexual overtones, no evidence of robbery, and a common denominator was that all victims were Caucasian and mostly from Italian-American heritage. The series of killings stopped as abruptly as they started and no viable suspect was ever developed.
14. The Servant Girl Annihilator
A series of eight ax-murders occurred in Austin, Texas in 1885 where the victims were young ladies who worked as servants to wealthy employers. All were chopped in their sleep in their detached quarters. Six victims were black. Two were white. No one was arrested in the cases and they also ended abruptly. In 2014, an investigative report for PBS identified a strong suspect as Nathan Elgin, a 19-year-old African-American cook who was known to many victims. Elgin was shot by police after attacking a similar servant girl with an ax. No other Austin ax-murders took place in this string after his death.
13. Frances Stewart Silver
“Frankie” Silver was hanged in 1833 for the ax-murder of her husband, Charles Silver. His dismembered body was found distributed around the family’s North Carolina farm. Frankie never confessed and, despite weak evidence, a jury convicted her. No motive was established. Prior to her execution, she was sprung from jail through a well-planned break and was disguised as a man. She was caught attempting to flee the state and returned to the gallows.
12. The Crazed Captain
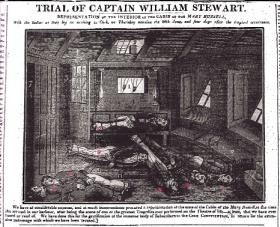 William Stewart was the skipper of the Mary Russell, a trading boat returning to England from Barbados. He suffered paranoid delusions and accused seven crew members of conspiring to mutiny. One by one, he lured the innocent men to the ship’s salon and enlisted three other young crew members to overpower the innocent men, binding them hand and foot then pinioning them to the floor. Once all seven were restrained, Captain Stewart took the ship’s fire-ax and systematically split their skulls. He was found not guilty by reason of insanity. The Mary Russell became known as the ship of seven murders.
William Stewart was the skipper of the Mary Russell, a trading boat returning to England from Barbados. He suffered paranoid delusions and accused seven crew members of conspiring to mutiny. One by one, he lured the innocent men to the ship’s salon and enlisted three other young crew members to overpower the innocent men, binding them hand and foot then pinioning them to the floor. Once all seven were restrained, Captain Stewart took the ship’s fire-ax and systematically split their skulls. He was found not guilty by reason of insanity. The Mary Russell became known as the ship of seven murders.
11. Karl Denke
By day, this guy was an organ player at a church in the Kingdom of Prussia. By night, he chopped people up with his ax and stored their flesh in huge vats of pickling salt. He was caught axing a man to death at Christmas in 1924. When police searched Denke’s home, they found his business ledger documenting 42 other humans Denke killed and commercially processed. He was selling the meat at the market labeled as salt-pork. Two days after his arrest, Dehke hung himself in jail.
10. The Tokoloshe
Elifasi Msomi was called The Ax Killer in his village in South Africa. He started an 18-month killing spree in 1953 where he raped and murdered six children by hacking them apart and disposing of their parts in a valley. When caught, he claimed to be possessed by an evil spirit called the Tokoloshe. Superstitious Zulu elders bought his claim and freed Msomi after exorcising the entity. When Msomi went back to business, higher authorities stepped in and re-arrested him. A psychological assessment found Msomi to be of very high intelligence, near brilliant, however derived sexual pleasure from inflicting pain and death upon young children. He got hung.
9. The Greenough Family Massacre
This took place in Greenough, Western Australia. In 1993, Karen MacKenzie and her three children Daniel (16), Amara (7), and Katrina (5) were so savagely ax-murdered on their remote rural farm that the trial judge ordered the details of the killings sealed, stating they were too gruesome for public knowledge. Bill Mitchell, their 24-year-old farmhand, was convicted in the murders as well as for performing sexual assaults on the dead bodies. He’s serving life sentences and was recently eligible for parole. It was denied.
8. The Hexing Axer
 Jake Bird, also known as the Tacoma Ax-Killer, was convicted in the 1947 murders of a mother and daughter in Tacoma, Washington. He got caught fleeing the scene, barefoot, after police were called to reports of horrific screams coming from the house. Bird had the victims’ blood and brain matter on his hands, feet, and clothes as well as his bloody fingerprints on the ax found by the bodies.
Jake Bird, also known as the Tacoma Ax-Killer, was convicted in the 1947 murders of a mother and daughter in Tacoma, Washington. He got caught fleeing the scene, barefoot, after police were called to reports of horrific screams coming from the house. Bird had the victims’ blood and brain matter on his hands, feet, and clothes as well as his bloody fingerprints on the ax found by the bodies.
At his sentencing to hang, Bird stated to the courtroom, “I’m putting the Jake Bird hex on all of you who had anything to do with my being punished. Mark my words, you will die before I do.”
 Allegedly, six of these people died before Bird was hung in 1949; the judge, the officer who interrogated Bird’s primary confession, the officer who interrogated a secondary confession to other murders, the court clerk, an attending guard, and Bird’s own defense lawyer. Bird progressively confessed to 46 other murders, saying he liked to use an ax because it did the job very well.
Allegedly, six of these people died before Bird was hung in 1949; the judge, the officer who interrogated Bird’s primary confession, the officer who interrogated a secondary confession to other murders, the court clerk, an attending guard, and Bird’s own defense lawyer. Bird progressively confessed to 46 other murders, saying he liked to use an ax because it did the job very well.
7. The Police Corruption Ax-Murder
Daniel Morgan was a private investigator who was digging into allegations of drug-related police corruption in the southeast section of London. In 1987, Morgan was found dead in a park with a massive ax-wound to the back of his head. This opened up a massive investigation into police corruption that resulted in five public inquiries. A number of officers have been charged with many offenses such as drug trafficking, extortion, conspiracy, and cover-ups, but who axed Daniel Morgan remains a secret. The investigation is ongoing.
6. Joseph Ntshongwana
Here’s another South African who was good with an ax. He was also good at sports, being a professional rugby player. But something wasn’t playing right in Joseph’s head. He convinced himself that four men gang-raped his daughter and gave her an HIV infection. He hunted and hacked the men, holding their heads as hostages. At his arraignment, Joe spoke in tongues and called to deities. The court called it faking insanity and declared him fit to stand trial. Joseph Ntshongwana’s now serving life… in maximum security.
5. Victor Licata
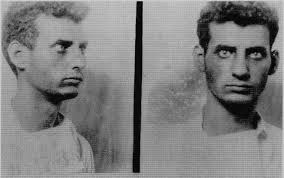 This guy did-in five members of his own family back in 1933. The Tampa, Flordia man was 21 when he went on a psychotic rampage and axed his way around the house. His mother, father, two brothers, a sister, and the family dog were slaughtered in their sleep. When arrested, Licata was dressed in clean clothes while his body underneath was covered with dried blood. Prior to the murders, his parents were trying to have him committed to a mental institute. They were too late. Licata eventually hung himself in a hospital for the criminally insane.
This guy did-in five members of his own family back in 1933. The Tampa, Flordia man was 21 when he went on a psychotic rampage and axed his way around the house. His mother, father, two brothers, a sister, and the family dog were slaughtered in their sleep. When arrested, Licata was dressed in clean clothes while his body underneath was covered with dried blood. Prior to the murders, his parents were trying to have him committed to a mental institute. They were too late. Licata eventually hung himself in a hospital for the criminally insane.
4. The Black Widow Ax-Murderer
 Eva Dugan was convicted of killing her fifth husband, Charlie, in Arizona back in the 1920’s. She, like others in this article, used an ax. Eva dismembered Charlie, then buried him in the desert. She was caught—I’m not sure how—and sentenced to hang. Eva became more famous in death because the hangman miscalculated and she was decapitated. They said Eva’s head came to a rolling stop in front of the witnesses, some of which fainted. The error led to Arizona adopting the gas chamber. The noose used to kill Eva Dugan is now on display at the Pinal County Historical Museum in Florence, Arizona.
Eva Dugan was convicted of killing her fifth husband, Charlie, in Arizona back in the 1920’s. She, like others in this article, used an ax. Eva dismembered Charlie, then buried him in the desert. She was caught—I’m not sure how—and sentenced to hang. Eva became more famous in death because the hangman miscalculated and she was decapitated. They said Eva’s head came to a rolling stop in front of the witnesses, some of which fainted. The error led to Arizona adopting the gas chamber. The noose used to kill Eva Dugan is now on display at the Pinal County Historical Museum in Florence, Arizona.
3. Lizzie Borden
 As the song goes, “Lizzie Borden took an ax and gave her mother forty whacks. When she saw what she had done, she gave her father forty-one.” This occurred in Fall River, Massachusetts in 1892. Lizzie Borden was acquitted of her parents’ murders, though history gives every indication she was dirty as a tree root. The motive appeared financial and Lizzie was perfectly sane. The house where the Borden murders took place is now a Bed & Breakfast / Museum and even has a giftshop where you can buy a Lizzie Borden Bobble Head doll. It’s blood-spattered and holding an ax. Now how cool is that? Click Here to visit or book a night.
As the song goes, “Lizzie Borden took an ax and gave her mother forty whacks. When she saw what she had done, she gave her father forty-one.” This occurred in Fall River, Massachusetts in 1892. Lizzie Borden was acquitted of her parents’ murders, though history gives every indication she was dirty as a tree root. The motive appeared financial and Lizzie was perfectly sane. The house where the Borden murders took place is now a Bed & Breakfast / Museum and even has a giftshop where you can buy a Lizzie Borden Bobble Head doll. It’s blood-spattered and holding an ax. Now how cool is that? Click Here to visit or book a night.
2. The Villisca Ax-Murders
 Probably the most famous ax-murder case… still unsolved… was in June of 1912. Six Moore family members and two child guests were savagely axed in a house in Villisca, Iowa. Evidence showed the killer hid in the attic and crept down while they slept, dispatching them one… by… one… a number of suspects… were identified… no one charged…. let alone convicted… motive unknown… crimes unsolved… the house is also a museum…
Probably the most famous ax-murder case… still unsolved… was in June of 1912. Six Moore family members and two child guests were savagely axed in a house in Villisca, Iowa. Evidence showed the killer hid in the attic and crept down while they slept, dispatching them one… by… one… a number of suspects… were identified… no one charged…. let alone convicted… motive unknown… crimes unsolved… the house is also a museum…
1. In The Attic
Now it’s my turn. I’m writing my next novel titled In The Attic. It’s based on the true double-ax-murders I investigated when I was a cop. Maria Dersch, the complainant/victim, came to my police office seeking protection from her ex-boyfriend, Billy Ray Shaughnessy. He’d just raped Maria at knife point, promised to kill her if caught with another man, then snuck back and sliced-up Maria’s clothes.
I’m the poor bastard who got handed the file.
 So, I took an audio-recorded statement from Maria. It opened “I’m so terrified that psycho’s going to kill me.” I went to Maria’s house to find Billy Ray. To arrest Billy Ray. To photo Maria’s clothes as evidence. He was nowhere to be found. I took this serious. I arranged for others to stay with Maria until Billy Ray could be caught… even arranged for the locks to be changed on Maria’s doors.
So, I took an audio-recorded statement from Maria. It opened “I’m so terrified that psycho’s going to kill me.” I went to Maria’s house to find Billy Ray. To arrest Billy Ray. To photo Maria’s clothes as evidence. He was nowhere to be found. I took this serious. I arranged for others to stay with Maria until Billy Ray could be caught… even arranged for the locks to be changed on Maria’s doors.
Two and a half days later, Maria and a male friend—Earl Barker, who stayed to protect Maria—were savagely slaughtered in their sleep. Billy Ray climbed down from the attic at 3 am with an ax. The scene looked like a bomb blasted a barrel of blood. He’d been in the attic… the whole fucking time… while I photographed the clothes… changed the locks… protected Maria…
In The Attic’s point of view tells in first-person with me, the nameless detective, narrating the investigation. Uniquely, it’s also told from Billy Ray’s perspective—his thoughts told to me about lurking above. In The Attic is nearly complete and I’m looking for potential victims who’d like ARC’s, Advance Reading Copies in exchange for reviews. In The Attic is available about mid-June in ePub, Mobi/Kindle, and PDF if anyone wants dibs.